The impact of academic anxiety on smartphone addiction among college students: the mediating role of self-regulatory fatigue and the moderating role of mindfulness
- PMID: 40205575
- PMCID: PMC11983919
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-025-02696-y
The impact of academic anxiety on smartphone addiction among college students: the mediating role of self-regulatory fatigue and the moderating role of mindfulness
Abstract
Background: Academic anxiety is recognized as a risk factor of smartphone addiction among college students. However, the underlying mechanisms and moderating factors remain insufficiently explored.
Method: This study examines the impact of academic anxiety on smartphone addiction, focusing on the mediating role of self-regulatory fatigue and the moderating role of mindfulness. Using convenience sampling strategy, a cross-sectional survey was implemented. Data were collected from a survey of 685 college students by using the Academic Anxiety Scale, Smartphone Addiction Scale, Self-Regulatory Fatigue Scale, and Mindfulness Scale. The hypothesized moderated mediation model was analyzed using Hayes' (2017) PROCESS macro (Model 59).
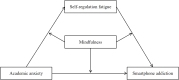
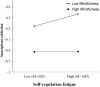
Results: Moderated mediation analysis finds that academic anxiety significantly positively predicts smartphone addiction (β = 0.30, t = 7.24, 95%CI=[0.22, 0.38], p<0.001) in college students. Academic anxiety also indirectly predicts smartphone addiction through self-regulatory fatigue (β = 0.09, t = 2.43, 95%CI=[0.02, 0.16], p<0.05), with the mediation effect accounting for 11.76%. The mediation pathways are moderated by mindfulness. Compared with students with low mindfulness, the influence of academic anxiety on self-regulatory fatigue is stronger in students with high mindfulness(β = 0.10, t = 3.85, 95%CI=[0.05, 0.16], p<0.001). However, compared with students with low mindfulness, the influence of self-regulatory fatigue on smartphone addiction is weaker in students with high mindfulness(β=-0.08, t= -2.53, 95%CI=[-0.15, -0.02], p<0.05). That is, among individuals with a high level of mindfulness, mindfulness enhances the positive relationship between academic anxiety and self-regulatory fatigue while weakening the positive association between self-regulatory fatigue and smartphone addiction.
Conclusion: These findings elucidate the internal mechanisms linking academic anxiety to smartphone addiction and underscoring the dual role of mindfulness. The results offer valuable insights for developing strategies to prevent and manage smartphone addiction among college students.
Keywords: Academic anxiety; College students; Mindfulness; Self-regulatory fatigue; Smartphone addiction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of The Fifth People’s Hospital Of Jiujiang (No.jjwy202423). Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Smartphone addiction and sleep quality in the physical activity-anxiety link: a mediation-moderation model.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 3;13:1512812. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1512812. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40247873 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of physical activity on smartphone addiction in Chinese college students-chain mediation of self-control and stress perception.BMC Public Health. 2025 Apr 24;25(1):1532. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22720-5. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40275263 Free PMC article.
-
Family happiness and college students' smartphone addiction control: the chain mediation effect of emotion regulation and self-control.Front Public Health. 2024 Oct 9;12:1444033. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1444033. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39444970 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Empirical Avoidance, Anxiety, Difficulty Describing Feelings and Internet Addiction Among College Students: A Moderated Mediation Model.J Genet Psychol. 2025 Jul-Aug;186(4):288-304. doi: 10.1080/00221325.2025.2453705. Epub 2025 Jan 21. J Genet Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39836109
-
The experiences in close relationship and internet addiction among college Students: A moderated mediation model of anxiety and information cocoon.Soc Sci Med. 2025 Feb;366:117641. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2024.117641. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Soc Sci Med. 2025. PMID: 39718279
References
-
- China Internet Network Information Center. The 55th Statistical Report on China’s Internet Development.https://www.cnnic.cn/n4/2025/0117/c88-11229.html, 2025-1-17.
-
- Chen L, Yan Z, Tang W, et al. Mobile phone addiction levels and negative emotions among Chinese young adults: the mediating role of interpersonal problems. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;55:856–66.
-
- Zhang MX, Wu AM. Effects of smartphone addiction on sleep quality among Chinese university students: the mediating role of self-regulation and bedtime procrastination. Addict Behav. 2020;111:106552. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical