Skin microbiome influences the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the immune system
- PMID: 40205611
- PMCID: PMC11980248
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-025-03791-5
Skin microbiome influences the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the immune system
Abstract
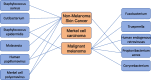
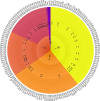
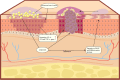
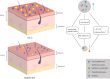
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is a type of skin tumor that develops in the epithelial cells. This disease has the second highest incidence of human skin cancers, with a high metastatic rate. While ultraviolet radiation significantly contributes to the genomic changes that support cSCC development, the dysbiosis of the skin microbiome and influence of the immune system also play important roles in this process. In this review, we discuss the effects of skin microbes and their metabolites on the immune system, including innate immune cells, T cells, and cytokines. We also discuss how Staphylococcus aureus and human papillomavirus can affect cSCC by impacting the immune system. Furthermore, we explore the antagonism of symbiotic microorganisms with cSCC-associated pathogens and their potential as novel therapeutic modalities.
Keywords: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; Immune system; Microbiome; Skin; Skin cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: N/A. Third party material: No, all of the material is owned by the authors and/or no permissions are required. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Winge MCG, Kellman LN, Guo K, et al. Advances in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023;23(7):430–49. 10.1038/s41568-023-00583-5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

