Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Dulaglutide in Mitigating Tacrolimus-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through Targeting the miR-22/HMGB-1/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Trajectory
- PMID: 40205909
- PMCID: PMC11983086
- DOI: 10.1002/ardp.202500023
Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Dulaglutide in Mitigating Tacrolimus-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through Targeting the miR-22/HMGB-1/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Trajectory
Abstract
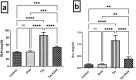
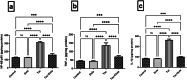
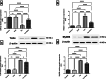
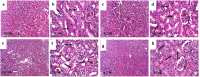
Tacrolimus (Tac) is an immunosuppressive drug used to reduce the risk of allograft rejection; however, it can induce renal injury. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB-1) protein, which induces inflammation through the aberrant stimulation of the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/myeloid differentiation primary response protein (MyD88)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) trajectory, could represent a molecular target for alleviating Tac-induced renal damage. The present study aimed to investigate the potential protective role of the GLP-1 agonist, dulaglutide (Dula), against Tac-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Rats were administered Tac (5 mg/kg/day) and vehicle or Dula (0.2 mg/kg once a week) for 14 days. Treatment with Dula reduced serum creatinine plus blood urea nitrogen and attenuated Tac-induced renal histopathological changes. Dula treatment also hampered renal inflammation and restored redox homeostasis, as indicated by remarkably reduced tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), malondialdehyde (MDA), and NADPH oxidase 1 levels alongside marked replenishment in reduced glutathione (GSH) content. These effects were mediated through the upregulation of miR-22 expression and the consequent inhibition of the HMGB-1/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB trajectory. Collectively, Dula has been demonstrated to protect rats against Tac-induced nephrotoxicity by reducing inflammation, restoring redox homeostasis, and modulation of the miR-22/HMGB-1/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB trajectory. Dula may be beneficial clinically in preventing Tac-induced renal injury.
Keywords: HMGB‐1; TLR4; dulaglutide; miR‐22; nephrotoxicity; tacrolimus.
© 2025 The Author(s). Archiv der Pharmazie published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of Deutsche Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effect of Dulaglutide, a GLP1 agonist, on acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats: involvement of GLP-1, TFF-3, and TGF-β/PI3K/NF-κB signaling pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May;398(5):5611-5628. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03631-5. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39579211 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapeutic role of astringin against chromium induced nephrotoxicity via modulating TLR4/MyD88, HMGB1/RAGE and NF-κB pathway: A biochemical and pharmacokinetic approach.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2025 Jun;89:127666. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2025.127666. Epub 2025 May 2. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40345103
-
The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways.Mol Immunol. 2018 Feb;94:7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.12.008. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29241031
-
The interplay of TapSAKI and NEAT-1 as potential modulators in gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury via orchestrating miR-22-3p/TLR4/MyD88/NF-қB/IL-1 β milieu: Novel therapeutic approach of Betanin.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;143(Pt 3):113577. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113577. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39541843
-
Dexmedetomidine Resists Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling.J Surg Res. 2021 Apr;260:350-358. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.11.041. Epub 2020 Dec 28. J Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 33383282
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

