Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for Twist1 Knockdown in 4T1 Cells
- PMID: 40205959
- PMCID: PMC12259407
- DOI: 10.1002/mabi.202400627
Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for Twist1 Knockdown in 4T1 Cells
Abstract
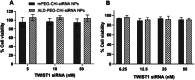
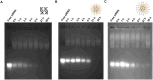
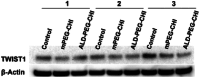
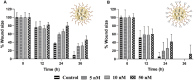
Bone metastasized breast cancer reduces the quality of life and median survival. Targeted delivery of twist1-siRNA using nanoparticles (NPs) is a promising strategy to overcome current limitations in treating such metastatic breast cancers. This research evaluates two types of chitosan (CHI)-based NPs for the delivery of twist1-siRNA. Alendronate conjugated PEG functionalized chitosan (ALD-PEG-CHI) NPs are developed for active targeting while PEG functionalized CHI (mPEG-CHI) NPs are fabricated for passive targeting. The size of twist1-siRNA-loaded NPs is below 70 nm and the zeta potential is near neutral for both types of NPs. Based on gel retardation assay, complete encapsulation of twist1-siRNA is achieved in both NP systems. The ALD-PEG-CHI-siRNA and mPEG-CHI-siRNA NPs display serum protection for 6 and 4 h, respectively, compared to the immediate degradation of naked twist1-siRNA. The NPs can knockdown twist1 in 4T1 cells as demonstrated through protein expression as well as by phenotypic change in directional cell migration by wound healing assay. Overall, these in vitro results illustrate the potential of the NPs as an effective therapeutic system for bone metastasized breast cancer.
Keywords: SiRNA delivery; chitosan; nanomedicine; poly(ethylene glycol); twist1.
© 2025 The Author(s). Macromolecular Bioscience published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeted Nanoparticles Based on Alendronate Polyethylene Glycol Conjugated Chitosan for the Delivery of siRNA and Curcumin for Bone Metastasized Breast Cancer Applications.Macromol Biosci. 2024 Feb;24(2):e2300268. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202300268. Epub 2023 Oct 15. Macromol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 37794635
-
Blockade of CD73 using siRNA loaded chitosan lactate nanoparticles functionalized with TAT-hyaluronate enhances doxorubicin mediated cytotoxicity in cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Sep 1;186:849-863. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.034. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. Retraction in: Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug;320(Pt 2):146069. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146069. PMID: 34245737 Retracted.
-
Cancer cell membrane-camouflaged pH-responsive nanoparticles for enhancing siRNA effect and synergistic anti-tumor therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 1;23(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03508-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40598479 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic delivery of siRNA for the management of breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer.Ther Deliv. 2024;15(11):871-891. doi: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2400044. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Ther Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39320858 Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Tahara R. K., Brewer T. M., Theriault R. L., Ueno N. T., Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance, (Ed: Ahmad A.), Springer, New York, NY, USA: 2019, pp. 105–129.
-
- Li J., Xue S., Mao Z.‐W., J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6620. - PubMed
-
- Mushtaq A., Li L., A. A., Grøndahl L., Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

