Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. polysaccharides exert anti-atopic dermatitis effects by modulating gut microbiota and the MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 40206087
- PMCID: PMC11978834
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1573135
Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. polysaccharides exert anti-atopic dermatitis effects by modulating gut microbiota and the MAPK/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
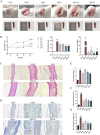
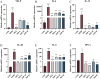
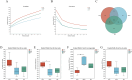
This study aims to extract polysaccharides from Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. (SSP) using alcohol and water extraction and investigate whether they can be delivered orally to treat atopic dermatitis (AD). In vivo investigations demonstrated that SSP notably improved inflammation in mice, reducing ear swelling, scratching frequency, mast cell infiltration, and epidermal thickness. Furthermore, it lowered the levels of associated inflammatory markers, increased the production of skin barrier-associated proteins, and restored gut microbial diversity, which altered the composition of bacterial communities. In vitro experiments demonstrated that SSP could diminish the levels of inflammatory factors in the human immortal keratinocyte line (HaCaT) and suppress the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Our results suggest SSP exerts anti-AD effects and regulates the gut-skin axis in mice. The anti-inflammatory mechanism involves the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. It is being tested for development into an effective drug for AD.
Keywords: Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham.; anti-inflammatory; atopic dermatitis; gut–skin axis; polysaccharides.
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Xie, Zhou, Chen, Zhou, Ding and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploring the gut microbiota mediated biotransformation of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham.: Insights from metabolite spectrum with UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS and bioinformatics analysis of gut microbiota metabolites.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Sep 1;247:116241. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116241. Epub 2024 May 22. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 38838440
-
Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo polysaccharide ameliorated DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis in mice associated with suppressing MAPK/NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118677. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118677. Epub 2024 Aug 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39121927
-
Extraction, partial characterization and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Apr 1;109:535-543. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.119. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29275205
-
Water Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham Ameliorates Pruritus by Inhibiting MrgprB2 Receptor.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Oct 27;15:5989-5998. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S384661. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36324862 Free PMC article.
-
Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham.: a review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Aug 26;149(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.048. Epub 2013 Jun 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23747644 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoid Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Damage via Activating the MyD88-Mediated Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway.Nutrients. 2025 Aug 1;17(15):2540. doi: 10.3390/nu17152540. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806124 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

