Neoadjuvant Targeted Therapy with Dacomitinib in a Stage IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patient Harboring EGFR G719X: A Case Report
- PMID: 40206237
- PMCID: PMC11980937
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S502112
Neoadjuvant Targeted Therapy with Dacomitinib in a Stage IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patient Harboring EGFR G719X: A Case Report
Abstract
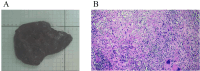
The effectiveness of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKIs) has been established, leading the NCCN Guidelines to recommend it as a first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, there is still controversy about the use of neoadjuvant TKI treatment for patients with stage III EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC. Here, we firstly report that a stage IIIA lung adenocarcinoma patient benefited from chemotherapy and dacomitinib as neoadjuvant targeted therapy based on EGFR G719X mutation, achieving a pathological downstaging and the chance of radical surgical resection. Our case describes dacomitinib use as neoadjuvant targeted therapy for EGFR positive advanced NSCLC and highlights the application of molecular testing for the better treatment decision making.
Keywords: EGFR G719X; NSCLC; dacomitinib; neoadjuvant targeted therapy; uncommon EGFR mutations.
© 2025 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation (EGFR) Testing for Prediction of Response to EGFR-Targeting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) Drugs in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(24):1-48. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074402 Free PMC article.
-
Dacomitinib in lung cancer: a "lost generation" EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor from a bygone era?Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 15;9:5641-53. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S52787. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26508839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with brain metastasis harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) G719X and L861Q mutations benefited from aumolertinib: two cases report and review of the literature.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 28;8(9):e10407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10407. eCollection 2022 Sep. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36119883 Free PMC article.
-
A real-world study of dacomitinib in later-line settings for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring EGFR mutations.Cancer Med. 2022 Feb;11(4):1026-1036. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4495. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35023313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xue J, Li B, Wang Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor combination therapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR-mutated, non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and bayesian network meta-analysis. Cancers. 2022;14(19):4894. doi:10.3390/cancers14194894 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Sequist LV, Geater SL, et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: a combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-lung 2, LUX-lung 3, and lux-lung 6. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:830–838. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00026-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

