Clinical Characteristics, Treatment Effects and Risk Factors of Liver Cirrhosis in Patients with Wilson's Disease Hepatic Type
- PMID: 40206275
- PMCID: PMC11976439
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00453
Clinical Characteristics, Treatment Effects and Risk Factors of Liver Cirrhosis in Patients with Wilson's Disease Hepatic Type
Abstract
Background and aims: Wilson's disease (WD) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that can be treated with medications. The lack of a single, specific diagnostic indicator leads to diagnostic difficulties, which may result in disease progression to cirrhosis and even liver cancer. Thus, this study aimed to analyze the clinical data, imaging, histopathological manifestations, genetic testing results, and treatment effects of patients with WD hepatic type, and to explore the factors related to WD cirrhosis.
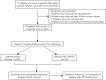
Methods: A single-center retrospective study was performed. 48 WD patients with a Leipzig score ≥ 4 were divided into a cirrhosis group and a non-cirrhosis group based on the presence of cirrhosis. Logistic regression analysis and odds ratios were used to describe the strength of association between risk factors and cirrhosis. The predictive value of the model for cirrhosis occurrence was evaluated by calculating the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and the cutoff value.
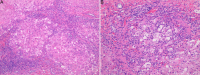
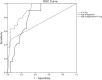
Results: All 48 patients diagnosed with WD had liver damage, with males accounting for 54.17%. The median age at diagnosis was 28 years (range: 10.25-40.5 years), and 39.58% of patients had cirrhosis. The most prevalent mutation was c.2333G>T (p.Arg778Leu), found in 41.30% (19/46) of cases. Imaging revealed fatty liver in 31.25% (15/48) of patients and "honeycomb-like" cirrhosis nodules in 73.68% (14/19). Compared with the non-cirrhosis group, the cirrhosis group had a higher positive rate for the Kayser-Fleischer (K-F) ring, older age at diagnosis, and higher levels of immunoglobulin G, but lower levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, white blood cells, and platelets (p < 0.05). Age at diagnosis (odds ratio = 1.072, 95% confidence interval = 1.007-1.142, p = 0.03) and the K-F ring (odds ratio = 18.657, 95% confidence interval = 1.451-239.924, p = 0.025) were independent risk factors for WD-related cirrhosis. The best values of area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for age at diagnosis combined with the K-F ring in predicting WD cirrhosis were 0.909. The average follow-up time for 33 patients was 48.6 months (range: 12-72 months). The biochemical recovery rate was over 60% after 12-72 months of treatment with zinc gluconate and/or penicillamine.
Conclusions: Age at diagnosis, combined with the K-F ring, is a simple and effective risk factor for WD-related cirrhosis. Zinc gluconate and penicillamine are safe and effective treatments.
Keywords: Age at diagnosis; K-F ring; Liver cirrhosis; Penicillamine; Wilson’s disease; Zinc gluconate.
© 2025 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maintenance zinc therapy after initial penicillamine chelation to treat symptomatic hepatic Wilson's disease in resource constrained setting.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan;37(1):31-38. doi: 10.1007/s12664-018-0829-x. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29457214
-
Construction of diagnostic prediction model for Wilson's disease.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 5;9:1065053. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1065053. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684333 Free PMC article.
-
Wilson's Disease: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Indian National Association for Study of the Liver, the Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, and the Movement Disorders Society of India.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Jan-Feb;9(1):74-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Sep 3. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30765941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The onset of psychiatric disorders and Wilson's disease].Encephale. 2007 Dec;33(6):924-32. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2006.08.009. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18789784 French.
-
Biomarkers for diagnosis of Wilson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 19;2019(11):CD012267. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012267.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31743430 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
