Real-world bleeding rates on emicizumab: the value of using nationwide digital treatment diary data in clinical research
- PMID: 40206324
- PMCID: PMC11981740
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpth.2025.102717
Real-world bleeding rates on emicizumab: the value of using nationwide digital treatment diary data in clinical research
Abstract
Background: People with hemophilia in the Netherlands log bleeds and infusions through a digital treatment diary. With the current innovations in hemophilia treatments, the use of patient-reported bleeding data will become increasingly important.
Objective: To assess real-world bleeding rates on emicizumab in a nationwide cohort of people with severe hemophilia A, and assess the value of digital treatment diary data.
Methods: People with severe hemophilia A of all ages with and without inhibitors using emicizumab who use the digital treatment diary were included. From 2018 to October 2023, data on bleeds treated with clotting factor concentrate were collected from digital treatment diaries and electronic health records. Mean (95% CI) annualized (joint) bleeding rates were calculated using negative-binomial regression analyses. Proportions of people with zero-treated (joint) bleeds were assessed using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. We calculated the proportion of all bleeds that were recorded in digital treatment diaries.
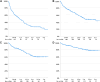
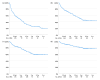
Results: The 232 included persons (median age, 27 years; IQR, 13-51) who used emicizumab for a median of 27 months (IQR, 14-31 months). The mean treated annualized bleeding rate and annualized joint bleeding rate were 1.5 (CI, 1.3-1.8) and 0.8 (CI, 0.6-1.0), respectively. At 24 weeks, 63% had zero-treated bleeds, and 80% had zero-treated joint bleeds. Of treated bleeds, 67% (310/460) were reported in digital treatment diaries.
Conclusion: Bleeding rates among Dutch people with severe hemophilia A using emicizumab were comparable to other real-world studies. We formulated recommendations to improve the quality of patient-reported bleeding data, such as establishing guidelines for recording bleeds and improving interoperability.
Keywords: emicizumab; hemophilia A; patient-generated health data; registries; telemedicine.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Blanchette V.S., Key N.S., Ljung L.R., Manco-Johnson M.J., van den Berg H.M., Srivastava A. Definitions in hemophilia: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:1935–1939. - PubMed
-
- Stichting HemoNED . Leiden; 2023. Rapportage gebruik emicizumab (Hemlibra)
-
- Oldenburg J., Mahlangu J.N., Kim B., Schmitt C., Callaghan M.U., Young G., et al. Emicizumab Prophylaxis in Hemophilia A with Inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:809–818. - PubMed
-
- Mahlangu J., Oldenburg J., Paz-Priel I., Negrier C., Niggli M., Mancuso M.E., et al. Emicizumab prophylaxis in patients who have hemophilia A without inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:811–822. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

