Forecasting readmission in COVID-19 patients utilizing blood biomarkers and machine learning in the Hospital-at-Home program
- PMID: 40206482
- PMCID: PMC11978629
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1469245
Forecasting readmission in COVID-19 patients utilizing blood biomarkers and machine learning in the Hospital-at-Home program
Abstract
Objectives: During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the Hospital-at-Home (HaH) program played a key role in expanding healthcare capacity and managing COVID-19 pneumonia. This study aims to evaluate the factors contributing to readmission from HaH to conventional hospitalization and to apply classification algorithms that support discharge decisions from conventional hospitalization to HaH.
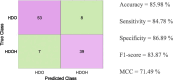
Methods: Blood biomarkers (IL-6, Hs-TnT, CRP, ferritin, and D-dimer) were collected from 871 patients transferred to HaH after conventional hospitalization for COVID-19 at the Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol. Of these, 840 patients completed their recovery without any complications, while 31 of them required readmission. Statistical tests were conducted to assess differences in blood biomarkers between the first day of conventional hospitalization and the first day of HaH, as well as between patients who successfully completed HaH and those who were readmitted. Various classification algorithms (bagged trees, KNN, LDA, logistic regression, Naïve Bayes, and the support vector machine [SVM]) were implemented to predict readmission, with performance evaluated using accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F1 score, and the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC).
Results: Significant differences were observed in IL-6, Hs-TnT, CRP (p < 0.001), and ferritin (p < 0.01) between the first day of conventional hospitalization and the first day of HaH for patients who were not readmitted. However, no significant differences were found in patients who were readmitted. At HaH, readmitted patients exhibited higher CRP and Hs-TnT values. Among the classification algorithms, the SVM showed the best performance, achieving 85% sensitivity, 87% specificity, 86% accuracy, 84% F1 score, and 71% MCC.
Conclusion: Hs-TnT was a key predictor of readmission for COVID-19 patients discharged to HaH. Classification algorithms can aid clinicians in making informed decisions regarding patient transfers from conventional hospitalization to HaH.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hospital-at-Home program; Hs-TnT; biomarkers; machine learning.
Copyright © 2025 Bonet-Papell, Company-Se, Delgado-Capel, Díez-Sánchez, Mateu-Pruñosa, Paredes-Deirós, Ara del Rey and Nescolarde.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Paulson MR, Torres-Guzman RA, Avila FR, Maita KC, Garcia JP, Forte AJ, et al. . Severity of illness and risk of mortality in Mayo Clinic’s virtual hybrid advanced care at home program: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Health Serv Res. (2023) 23:287. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09333-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artico J, Shiwani H, Moon JC, Gorecka M, McCann GP, Roditi G, et al. . Myocardial involvement after hospitalization for COVID-19 complicated by troponin elevation: A prospective, multicenter, Observational Study. Circulation. (2023) 147:364–74. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060632, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

