Multidimensional regulation of transcription factors: decoding the comprehensive signals of plant secondary metabolism
- PMID: 40206880
- PMCID: PMC11979206
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1522278
Multidimensional regulation of transcription factors: decoding the comprehensive signals of plant secondary metabolism
Abstract
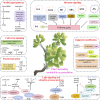
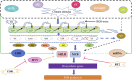
Plants synthesize an extensive array of secondary metabolites in response to diverse biotic and abiotic stresses. These metabolites function not only as defensive compounds but also constitute significant sources of nutrition and pharmaceuticals. However, the mechanisms governing the synthesis of these secondary metabolites have long been a central focus of research and continue to pose significant challenges. Transcription factors (TFs), serving as key regulators of secondary metabolite synthesis in plants, exhibit mechanisms of action that are still not fully understood. This review summarizes the latest research advancements on how plant transcription factors mediate the regulation of secondary metabolite biosynthesis through various signaling pathways, including light signaling, hormone signaling, MAPK signaling, the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, epigenetic regulation, microbial interactions, and climate change. A deeper understanding of the mechanisms regulating transcription factors is expected to provide new insights into the biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites.
Keywords: biosynthesis; mechanisms; secondary metabolites; signaling pathways; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Chen, Zhang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmadzadeh M., Keshtkar A. H., Moslemkhany K., Ahmadzadeh M. (2022). Effect of the plant probiotic bacteria on terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis pathway gene expression profiling, vinblastine and vincristine content in the root of Catharanthus roseus . Mol. Biol. Rep. 49, 10357–10365. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07841-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- An J. P., Zhao L., Cao Y. P., Ai D., Li M. Y., You C. X., et al. (2024). The SMXL8-AGL9 module mediates crosstalk between strigolactone and gibberellin to regulate strigolactone-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Cell. 36 (10), 4404–4425. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae191 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

