The Effectiveness of Telehealth Intervention on Chronic Kidney Disease Management in Adults: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40207003
- PMCID: PMC11975977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpdig.2024.11.002
The Effectiveness of Telehealth Intervention on Chronic Kidney Disease Management in Adults: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of telehealth programs on dietary habits, quality of life, renal function, and blood pressure in adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
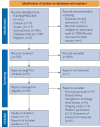
Patients and methods: A systematic literature review was completed according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. Using PubMed/Medline, Scopus, Embase, and ScienceDirect databases, articles published between 2012 and 2024 were selected using the following keywords: telehealth, eHealth, mHealth, telemedicine, telenutrition, and chronic kidney disease.
Results: A total of 13 studies-10 randomized controlled trials and 3 single-arm trials-were chosen for this review. In these trials, telehealth interventions were administered using mobile applications, phone calls, web-based communications, text messaging, wearable devices, or a combination of these tools to provide treatment for adults with CKD. Interdisciplinary collaboration between a dietitian and other health care team members was shown to improve renal function and dietary habits when providing telehealth interventions via mobile applications, phone calls, and text messaging. Web-based telehealth delivery that involves diverse health care personnel has been shown to improve the quality of life in adult patients with CKD.
Conclusion: Receiving treatment using telehealth communication methods may be a beneficial option for adult patients with CKD by enhancing accessibility, promoting multidisciplinary collaboration, and effectively managing blood pressure and dietary habits, leading to improved quality of life for patients. Future research administering homogeneous and rigorously controlled experimental methods with larger and more diverse populations, as well as longer study durations, is necessary to further elucidate the effectiveness of CKD treatment delivery via telehealth for adult patients.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of telehealth-delivered nutrition interventions: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Rev. 2023 Nov 10;81(12):1599-1611. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad032. Nutr Rev. 2023. PMID: 37016937 Free PMC article.
-
A Coaching Program to Improve Dietary Intake of Patients with CKD: ENTICE-CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Mar 6;15(3):330-340. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12341019. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32111701 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Telehealth-Supported Exercise or Physical Activity Programs for Knee Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Aug 2;26:e54876. doi: 10.2196/54876. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39094114 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
eHealth interventions for people with chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Aug 6;8(8):CD012379. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012379.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31425608 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emerging Biomarkers and Advanced Diagnostics in Chronic Kidney Disease: Early Detection Through Multi-Omics and AI.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 13;15(10):1225. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15101225. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Metabolic Medicine: A Narrative Review of Insights and Innovations for the Future.Diabetes Ther. 2025 Jun;16(6):1155-1176. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01738-3. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40272772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources