Artificial Intelligence for Kidney Stone Spectra Analysis: Using Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Quality Assurance in the Clinical Laboratory
- PMID: 40207142
- PMCID: PMC11975758
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpdig.2023.01.001
Artificial Intelligence for Kidney Stone Spectra Analysis: Using Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Quality Assurance in the Clinical Laboratory
Abstract
Objective: To determine if a set of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms could be leveraged to interpret Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra and detect potentially erroneous stone composition results reported in the laboratory information system by the clinical laboratory.
Background: Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones) is highly prevalent, causes significant pain, and costs billions of dollars annually to treat and prevent. Currently, FTIR is considered the reference method for clinical kidney stone constituent analysis. This process, however, involves human interpretation of spectra by a qualified technologist and is susceptible to human error.
Methods: This prospective validation study was conducted from October 29, 2020, to October 28, 2021, to test if the addition of AI algorithm overreads to FTIR spectra could improve the detection rate of technologist-misclassified FTIR spectra. The preceding year was used as a control period. Disagreement between the AI overread and technician interpretation was resolved by an independent human interpretation. The rate of verified human misclassifications that resulted in revised reported results was the primary end point.
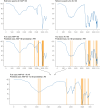
Results: Spectra of 81,517 kidney stones were reviewed over the course of 1 year. The overall clinical concordance between the technologist and algorithm was 90.0% (73,388/81,517). The report revision rate during the AI implementation period was nearly 8 times higher than that during the control period (relative risk, 7.9; 95% CI, 4.1-15.2).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that an AI quality assurance check of human spectra interpretation resulted in the identification of a significant increase in erroneously classified spectra by clinical laboratory technologists.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AI-Augmented Kidney Stone Composition Analysis with Auto-Release Improves Quality, Efficiency, Cost-Effectiveness, and Staff Satisfaction.J Appl Lab Med. 2025 Mar 3;10(2):305-314. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfae146. J Appl Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39700400
-
Are conventional stone analysis techniques reliable for the identification of 2,8-dihydroxyadenine kidney stones? A case series.Urolithiasis. 2020 Aug;48(4):337-344. doi: 10.1007/s00240-020-01187-6. Epub 2020 May 12. Urolithiasis. 2020. PMID: 32399606 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Chest Radiograph Interpretations by Artificial Intelligence Algorithm vs Radiology Residents.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Oct 1;3(10):e2022779. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.22779. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33034642 Free PMC article.
-
UrologiQ: AI-based accurate detection, measurement and reporting of stones in CT-KUB scans.Urolithiasis. 2024 Nov 28;52(1):170. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01671-3. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 39607513 Review.
-
Can Artificial Intelligence Accurately Detect Urinary Stones? A Systematic Review.J Endourol. 2024 Aug;38(8):725-740. doi: 10.1089/end.2023.0717. Epub 2024 May 30. J Endourol. 2024. PMID: 38666692
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

