Arthroscopic "Crisscross" Fixation Technique for Avulsion Fracture of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament From the Tibia
- PMID: 40207346
- PMCID: PMC11977143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2024.103277
Arthroscopic "Crisscross" Fixation Technique for Avulsion Fracture of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament From the Tibia
Abstract
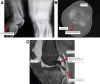
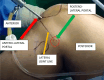
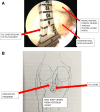
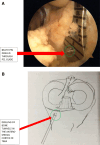
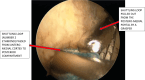
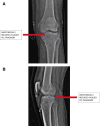
This study describes a method of fixing posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) avulsion fractures called the arthroscopic crisscross technique. PCL avulsion fracture is a rare injury that generally occurs in young patients. A displaced avulsion fracture at the tibial attachment of the PCL is an indication for surgical reduction and internal fixation given that nonunion, posterior instability, and early degenerative changes of the knee are common consequences of conservative treatment. This study describes all-arthroscopic fixation of the PCL avulsion injury using 2 No. 2 FiberTape sutures (nonabsorbable polyblend; Arthrex) via the arthroscopic crisscross technique. The No. 2 FiberTapes crisscross each other over the avulsed fragment. Through tensioning of both No. 2 FiberTapes, they are fixed anteriorly using a suture button. This technique can be considered a safe and effective method using minimal resources for the fixation of the avulsed PCL from its tibial footprint.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Schulz M.S., Russe K., Weiler A., Eichhorn H.J., Strobel M.J. Epidemiology of posterior cruciate ligament injuries. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Littlejohn S.G., Geissler W.B. Arthroscopic repair of a posterior cruciate ligament avulsion. Arthroscopy. 1995;11:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Griffith J.F., Antonio G.E., Tong C.W., Ming C.K. Cruciate ligament avulsion fractures. Arthroscopy. 2004;20:803–812. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

