PII protein is essential for transcriptional regulation of anf gene cluster for iron-only nitrogenase in Rhodopseudomonas palustris
- PMID: 40207968
- PMCID: PMC12093980
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.00465-25
PII protein is essential for transcriptional regulation of anf gene cluster for iron-only nitrogenase in Rhodopseudomonas palustris
Abstract
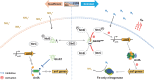
In addition to catalyzing the biological nitrogen fixation, iron-only (Fe-only) nitrogenase is also able to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) to formate (HCOO-) and methane (CH4). AnfA is responsible for the transcriptional activation of the anf gene cluster for Fe-only nitrogenase, whose expression is repressed by fixed nitrogen. However, it remains unclear how AnfA is regulated to control the expression of Fe-only nitrogenase. Here, we found that in Rhodopseudomonas palustris, PII proteins play a critical role in regulating the expression of Fe-only nitrogenase genes via AnfA. We hypothesize that the deuridylylated PII protein GlnK1, which was upregulated in the presence of ammonium (NH4+), could inhibit AnfA activity by forming a potential AnfA-GlnK1 complex. This likely serves as a fail-safe mechanism to prevent R. palustris from expressing Fe-only nitrogenase when AnfA is accidentally expressed under nitrogen-excess conditions. The uridylylated PII protein GlnK2UMP, which was upregulated in response to nitrogen starvation, stimulated the expression of an active AnfA hexamer that further activated the expression of Fe-only nitrogenase under nitrogen-fixing and Mo-free conditions. This study provides new insights into the regulation of Fe-only nitrogenase in R. palustris.IMPORTANCEThe expression and maturation of nitrogenase are tightly regulated by ambient nitrogen levels, which limits the persistence and efficiency of biological nitrogen fixation. This study offers new insights into the regulatory mechanism of AnfA by PII proteins in Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Understanding the regulation of AnfA, the transcriptional activator of the Fe-only nitrogenase gene cluster, could provide strategies to better control the expression of iron-only nitrogenase. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria that constitutively express iron-only nitrogenase have the potential to be developed into promising biofertilizers, as their nitrogen-fixing activity is enhanced and independent of molybdenum availability in the soil.
Keywords: Fe-only nitrogenase; PII proteins; Rhodopseudomonas; gene regulation; photosynthetic bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Formation of NifA-PII complex represses ammonium-sensitive nitrogen fixation in diazotrophic proteobacteria lacking NifL.Cell Rep. 2024 Jul 23;43(7):114476. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114476. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38985671
-
Functional genomic analysis of three nitrogenase isozymes in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris.J Bacteriol. 2005 Nov;187(22):7784-94. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.22.7784-7794.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16267302 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of pII family (GlnK1, GlnK2, and GlnB) protein uridylylation in response to nitrogen availability for Rhodopseudomonas palustris.Anal Biochem. 2006 Oct 1;357(1):93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2006.05.038. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Anal Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16860774
-
Regulation of nitrogen fixation in the phototrophic purple bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 May;4(3):243-8. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11931554 Review.
-
PII signal transduction proteins: pivotal players in post-translational control of nitrogenase activity.Microbiology (Reading). 2012 Jan;158(Pt 1):176-190. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.049783-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 22210804 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 32070034, 92351302, 91851102, 32270056/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32300032/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- XDA28030201/Bureau of Science and Technology for Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 2020YFA0906800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2105300/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

