Microbial diversity and fitness in the gut-brain axis: influences on developmental risk for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40207973
- PMCID: PMC11988266
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2486518
Microbial diversity and fitness in the gut-brain axis: influences on developmental risk for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
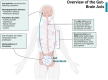
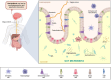
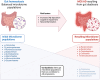
The gut-brain axis (GBA) denotes the dynamic and bidirectional communication system that connects the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system (CNS). This review explored this axis, focusing on the role of microbial diversity and fitness in maintaining gastrointestinal health and preventing neurodegeneration, particularly in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Gut dysbiosis, characterized by the imbalance in populations of beneficial and harmful bacteria, has been associated with increased systemic inflammation, neuroinflammation, and the progression of AD through pathogenic mechanisms involving amyloid deposition, tauopathy, and increased blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Emerging evidence highlighted the therapeutic potential of probiotics, dietary interventions, and intermittent fasting in restoring microbial balance, reducing inflammation, and minimizing neurodegenerative risks. Probiotics and synbiotics are promising in helping improve cognitive function and metabolic health, while dietary patterns like the Mediterranean diet were linked to decreased neuroinflammation and enhanced gut-brain communication. Despite significant advancement, further research is needed to elucidate the specific microbial strains, metabolites, and mechanisms influencing brain health. Future studies employing longitudinal designs and advanced omics technologies are essential to developing targeted microbiome-based therapies for managing AD-related disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; gut dysbiosis; gut-brain axis; microbial diversity; microbiota-gut-brain axis; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroinflammation; neuromodulators; probiotics; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
