Activin Actions in Adipocytes
- PMID: 40208114
- PMCID: PMC12192441
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf233
Activin Actions in Adipocytes
Abstract
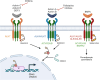
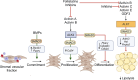
Obesity is a growing global health problem characterized by excess fat accumulation. Though causes of obesity are multifactorial, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists have emerged as effective weight loss drugs. Nevertheless, these agents are expensive, not uniformly available, and must be used continuously. Moreover, side effects and low efficacy limit the use of these and related molecules in some individuals. Therefore, there is continued interest in characterizing mechanisms regulating adiposity to aid in the development of novel treatments. In recent years, there has been a growing appreciation for ligands of the TGFβ family, the activins, in adipocyte proliferation, differentiation, and function. Here, we review recent progress in understanding the role of these molecules, with a particular focus on the hepatokine, activin E, in lipolysis and diet-induced obesity.
Keywords: TGFβ; adipose; ligand; lipolysis; obesity.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Drolet R, Richard C, Sniderman AD, et al. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of abdominal adipose tissues in women. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008;32(2):283‐291. - PubMed
-
- Hagberg CE, Spalding KL. White adipocyte dysfunction and obesity-associated pathologies in humans. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(4):270‐289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

