Artificial Intelligence as a New Research Ally? Performing AI-Assisted Systematic Literature Reviews in Health Economics
- PMID: 40208557
- PMCID: PMC12081476
- DOI: 10.1007/s40273-025-01481-4
Artificial Intelligence as a New Research Ally? Performing AI-Assisted Systematic Literature Reviews in Health Economics
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Funding: The authors declare that no funds, grants or other support were received during the preparation of this research letter. Conflicts of Interest: Sietse van Mossel, Martijn Johan Oude-Wolcherink, Rafael Emilio de Feria Cardet, Lioe-Fee de Geus-Oei, Dennis Vriens, Hendrik Koffijberg and Sopany Saing have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this research letter. Ethics Approval: Not applicable. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Availability of Data and Material: The software codes and datasets generated/analysed on which the reported results in this research letter rely are publicly available using the following Zenodo link: https://zenodo.org/record/8217881 . The originally published search strategies and title/abstract screening criteria are publicly available using the following https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-024-01447-y . Code Availability: The software codes on which the reported results in this research letter rely are publicly available using the following Zenodo link: https://zenodo.org/record/8217881 . Authors’ Contributions: All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by SvM and MOW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SvM and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Figures
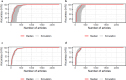
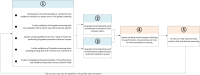
Similar articles
-
Ambient Assisted Living: Scoping Review of Artificial Intelligence Models, Domains, Technology, and Concerns.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Nov 4;24(11):e36553. doi: 10.2196/36553. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 36331530 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy for inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and new horizons.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 10;14:17562848211017730. doi: 10.1177/17562848211017730. eCollection 2021. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34178115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence-assisted interventions for perioperative anesthetic management: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02699-z. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39232648 Free PMC article.
-
Exponential growth of systematic reviews assessing artificial intelligence studies in medicine: challenges and opportunities.Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 28;11(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-01984-7. Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35761303 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in COVID-19 evidence syntheses was underutilized, but impactful: a methodological study.J Clin Epidemiol. 2022 Aug;148:124-134. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.04.027. Epub 2022 May 2. J Clin Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35513213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cosby K, Yang D, Fineberg HV. Assessing diagnostic performance. NEJM Evid. 2024. 10.1056/EVIDra2300232. - PubMed
-
- Blaizot A, Veettil SK, Saidoung P, Moreno-Garcia CF, Wiratunga N, Aceves-Martins M, et al. Using artificial intelligence methods for systematic review in health sciences: a systematic review. Res Synth Methods. 2022;13:353–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

