Rules of engagement for condensins and cohesins guide mitotic chromosome formation
- PMID: 40208986
- PMCID: PMC12118822
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adq1709
Rules of engagement for condensins and cohesins guide mitotic chromosome formation
Abstract
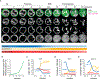
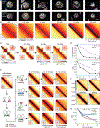
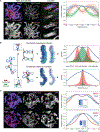
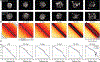
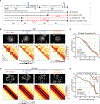
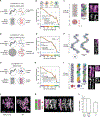
We used Hi-C, imaging, proteomics, and polymer modeling to define rules of engagement for SMC (structural maintenance of chromosomes) complexes as cells refold interphase chromatin into rod-shaped mitotic chromosomes. First, condensin disassembles interphase chromatin loop organization by evicting or displacing extrusive cohesin. Second, condensin bypasses cohesive cohesins, thereby maintaining sister chromatid cohesion as sisters separate. Studies of mitotic chromosomes formed by cohesin, condensin II, and condensin I alone or in combination lead to refined models of mitotic chromosome conformation. In these models, loops are consecutive and not overlapping, implying that condensins stall upon encountering each other. The dynamics of Hi-C interactions and chromosome morphology reveal that during prophase, loops are extruded in vivo at ∼1 to 3 kilobases per second by condensins as they form a disordered discontinuous helical scaffold within individual chromatids.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
Rules of engagement for condensins and cohesins guide mitotic chromosome formation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 30:2024.04.18.590027. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.18.590027. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Science. 2025 Apr 11;388(6743):eadq1709. doi: 10.1126/science.adq1709. PMID: 38659940 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hirano T, Condensin-Based Chromosome Organization from Bacteria to Vertebrates. Cell (2016). - PubMed
-
- Yatskevich S, Rhodes J, Nasmyth K, Organization of Chromosomal DNA by SMC Complexes. Annu Rev Genet (2019). - PubMed
-
- Hoencamp C, Rowland BD, Genome control by SMC complexes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

