A frameshift-generated cancer neoepitope that controls tumor burden in prophylaxis as well as therapy
- PMID: 40209093
- PMCID: PMC12207075
- DOI: 10.1093/jimmun/vkaf016
A frameshift-generated cancer neoepitope that controls tumor burden in prophylaxis as well as therapy
Abstract
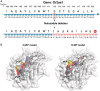
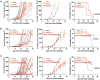
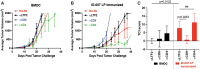
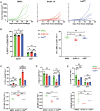
Insertion or deletion of one or two base pairs within a coding region causes a frameshift, which has the potential to generate neoepitopes (InDel-generated neoepitopes) that lack a self-counterpart and are entirely novel. Despite the obvious appeal of InDel-generated neoepitopes, and the demonstration of such candidate neoepitopes that can elicit a CD8 T-cell response, no InDel-generated neoepitopes that actually control tumors in vivo have been reported thus far. Here, in a mouse colon carcinoma line, we identify 11 InDels, only one of which generates a neoepitope that elicits tumor control in vivo in models of prophylaxis as well as therapy. Although this neoepitope has no self-counterpart, it has a low affinity (IC50 33,937.60 nM) for its MHC I allele. Despite its low affinity for MHC I, this neoepitope elicits antitumor activity in vivo through CD8 T cells. Furthermore, CD8 T cells elicited by this InDel-generated neoepitope, like the neoepitopes created by point mutations, show notably less exhaustion than classical immunogenic epitopes. Ironically, this InDel-generated neoepitope follows the same rules as noted for most of the tumor control-mediating neoepitopes generated by point mutations that have a poor affinity for MHC I alleles.
Keywords: InDel; cancer antigen; cancer vaccine; neoantigen; tumor-specific antigen.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The American Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
P.K.S. is a founder of Agenus and a founder, board member, and stock owner of Life Science Pharmaceuticals. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

