Impact of Excess Activin A on the Lipids, Metabolites, and Steroids of Adult Mouse Reproductive Organs
- PMID: 40209098
- PMCID: PMC12000649
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf054
Impact of Excess Activin A on the Lipids, Metabolites, and Steroids of Adult Mouse Reproductive Organs
Abstract
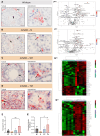
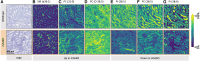
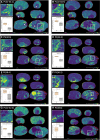
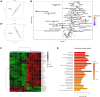
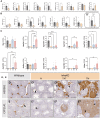
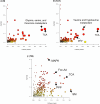
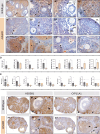
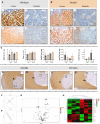
Bioactivity of the hormone and growth factor activin A is central to fertility and health. Dysregulated circulating activin levels occur with medication usage and multiple pathological conditions. The inhibin-alpha knockout mouse (InhaKO) models chronic activin elevation and unopposed activin A bioactivity. In InhaKO fetal testes, lipid droplet, steroid profiles, and seminiferous cords are abnormal; adults develop gonadal and adrenal tumors due to chronic activin A excess exposure. Here we address how this exposure affects lipid, metabolite, and steroid composition in whole testes, ovaries, and adrenals of adult InhaKO mice using histological, transcriptomic, and mass spectrometry (MS) methods, including MS imaging (matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-MS imaging). Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-MS imaging delineated spatial lipid profiles within interstitial, inner cord, and outer cord regions containing normal spermatogenesis; these differed between wild-type and KO samples. In proximity to tumors, lipids showed distinctive distribution patterns both within and adjacent to the tumor. Significantly altered lipids and metabolic profiles in whole InhaKO testes homogenates were linked to energy-related pathways. In gonads and adrenal glands of both sexes, steroidogenic enzyme transcription, and steroids are different, as expected. Lipid profiles and steroidogenic enzyme proteins, HSD3B1 and CYP11A1, are affected within and near gonadal tumors. This documents organ-specific effects of chronic activin A elevation on lipid composition and cellular metabolism, in both histologically normal and tumor-affected areas. The potential for activin A to influence numerous steroidogenic processes should be considered in context and with spatial precision, particularly in relationship to pathologies.
Keywords: activin A; adrenal gland; lipid metabolism; mass spectrometry; ovary; steroids; testis; testosterone.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Testis exposure to unopposed/elevated activin A in utero affects somatic and germ cells and alters steroid levels mimicking phthalate exposure.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 1;14:1234712. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1234712. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37727456 Free PMC article.
-
Activin induces x-zone apoptosis that inhibits luteinizing hormone-dependent adrenocortical tumor formation in inhibin-deficient mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;23(11):3951-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.11.3951-3964.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12748296 Free PMC article.
-
Activin A Determines Steroid Levels and Composition in the Fetal Testis.Endocrinology. 2020 Jul 1;161(7):bqaa058. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa058. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32274496
-
Activins in reproductive biology and beyond.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Apr;22(3):342-57. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv058. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 26884470 Review.
-
Regulation of activin and inhibin in the adult testis and the evidence for functional roles in spermatogenesis and immunoregulation.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Aug 15;359(1-2):30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.09.031. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21964464 Review.
References
-
- Wijayarathna R, de Kretser DM. Activins in reproductive biology and beyond. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22(3):342‐357. - PubMed
-
- Reis F. Activin A in mammalian physiology. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):739‐780. - PubMed
-
- Bellissima V, Visser GHA, Ververs TF, et al. Antenatal maternal antidepressants drugs affect activin A concentrations in maternal blood, in amniotic fluid and in fetal cord blood. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;24(sup2):31‐34. - PubMed
-
- Spencer K, Cowans NJ, Nicolaides KH. Maternal serum inhibin-A and activin-A levels in the first trimester of pregnancies developing pre-eclampsia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008;32(5):622‐626. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

