Comparative transcriptome analysis of Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822) from polluted and non-polluted rivers in India
- PMID: 40209169
- PMCID: PMC11984975
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320358
Comparative transcriptome analysis of Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822) from polluted and non-polluted rivers in India
Abstract
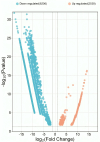
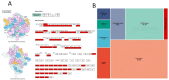
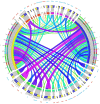
Labeo calbasu (L. calbasu) is an important detrivore fish in an ecosystem. So, the present transcriptome study was undertaken in relation to polluted and non-polluted water sources from a natural perennial river system. The Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform was used to perform transcriptome analysis on liver samples of L. calbasu that were collected from the Ganga and Yamuna rivers. From 8744 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), 2538 were upregulated, and 6206 were downregulated in response to pollution stress. Biologic process (BP), cellular component (CC), molecular function (MF), and Gene Ontology (GO) demonstrated that relevant genes were associated with peptide metabolic process, cytosol, RNA binding, etc. In the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome (KEGG) analysis, ribosomal and metabolic pathways were more important due to the high False discovery rate (FDR) and the involvement of many genes. Transcripts of uncertain coding potential (TUCP) and various RNAs like mRNAs and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) orchestrate fish cellular responses to environmental stressors in polluted waters, where aquatic ecosystems are threatened. FGG mRNA is co-expressed in both up and down-regulation in the liver of L. calbasu. In conclusion, L. calbasu collected from the Yamuna River have highly pollution-induced ribosomal pathways involving genes like Rpl19, rpl23Ae, rps2e, rps10e, rps15e, and rps7e, etc, which is important for pollution biomarker study. RANBP2 and egr1 lncRNA are the most significantly interlinked with ndc1 and fosab lncRNA.
Copyright: © 2025 Pradhan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stock assessment of fish species Labeo rohita, Tor tor and Labeo calbasu in the rivers of Vindhyan region, India.J Environ Biol. 2012 Mar;33(2):261-4. J Environ Biol. 2012. PMID: 23033691
-
Transcriptome analysis of long noncoding RNAs ribonucleic acids from the livers of Hu sheep with different residual feed intake.Animal. 2021 Feb;15(2):100098. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2020.100098. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Animal. 2021. PMID: 33573993
-
Transcriptomic responses to pollution in natural riverine environment in Rita rita.Environ Res. 2020 Jul;186:109508. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109508. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 32325295
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals immunoregulation mechanism of lncRNA-mRNA in gill and skin of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in response to Cryptocaryon irritans infection.BMC Genomics. 2022 Mar 15;23(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08431-w. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35287569 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of mitochondrial ATPase 6/8 genes in wild Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822) and mapping of natural genetic diversity.Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2016 Sep;27(5):3078-81. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2014.1003917. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2016. PMID: 25630739
References
-
- Imran S, Thakur S, Jha DN, Dwivedi AC. Size composition and exploitation pattern ofLabeo calbasu (Hamilton 1822) from the lower stretch of the Yamuna river. AJBS. 2015;10(2):171–3. doi: 10.15740/has/ajbs/10.2/171-173 - DOI
-
- Amitabh Chandra D, Prakash N. Age and growth increment of Labeo calbasu (Hamilton 1822) from the Vindhyan region, Central India. Int J Aquac Fish Sci. 2021;010–3. doi: 10.17352/2455-8400.000067 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

