Arterial spin labeling MRI based perfusion pattern related to motor dysfunction and L-DOPA reactivity in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40209569
- PMCID: PMC12008145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2025.103776
Arterial spin labeling MRI based perfusion pattern related to motor dysfunction and L-DOPA reactivity in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
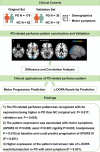
Objective: Identifying intrinsic pattern of Parkinson's disease (PD) helps to better understand of PD and provide insights to disease identification and treatment monitoring. Here we confirmed the PD-related covariance pattern (PDRP) by using arterial spin labelling technology (ASL-PDRP) and explore its potential for predicting motor progression and levodopa (L-DOPA) reactivity reduction.
Methods: Data from an original cohort of 179 PD and 62 normal controls (NC) and a validation cohort including 36 PD and 19 NC to construct and validate the ASL-PDRP. The correlations between the pattern and motor symptoms were analyzed cross-sectionally and longitudinally (71 PD owned longitudinal data) with hierarchical linear regression analysis. Kaplan-Meier analysis was conducted in 54 L-DOPA-managed PD patients to predict the levodopa reactivity reduction.
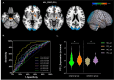
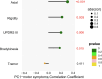
Results: The first principal component was predominantly recognized as the ASL-PDRP, with its expression being higher in PD than NC in both sets (original: P = 0.017, AUC = 0.598; validation: P = 0.024, AUC = 0.661). The pattern expression was associated with UPDRS III (P = 0.006) and sub-symptoms (axial: P < 0.001; rigidity: P = 0.003; bradykinesia: P = 0.015) at baseline. The ASL-PDRP could predict the progression of UPDRS III (P = 0.021, β = 4.930). Higher expression of the pattern had slower rate of levodopa reactivity reduction in PD patients with axial symptom (P = 0.031).
Conclusion: The identified ASL-PDRP may have potential for characterizing PD with the ability to predict motor progression and L-DOPA reactivity reduction.
Keywords: Arterial spin labelling; Levodopa reactivity; Magnetic resonance imaging; Motor symptoms; Neuroimaging; Parkinson’s disease; Pattern.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

