FFAR4-mediated IL-6 release from islet macrophages promotes insulin secretion and is compromised in type-2 diabetes
- PMID: 40210633
- PMCID: PMC11986018
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58706-5
FFAR4-mediated IL-6 release from islet macrophages promotes insulin secretion and is compromised in type-2 diabetes
Abstract
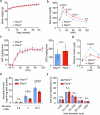
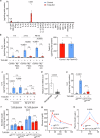
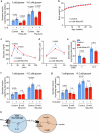
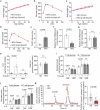
The function of islet macrophages is poorly understood. They promote glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in lean mice, however, the underlying mechanism has remained unclear. We show that activation of the free fatty acid receptor FFAR4 on islet macrophages leads to interleukin-6 (IL-6) release and that IL-6 promotes β-cell function. This mechanism is required for GSIS in lean male mice, but does not function anymore in islets from people with obesity and obese type 2 diabetic male mice. In islets from obese mice, FFAR4 downstream signaling in macrophages is strongly reduced, resulting in impaired FFAR4-mediated IL-6 release. However, IL-6 treatment can still improve GSIS in islets from people with obesity and obese type 2 diabetic mice. These data show that a defect in FFAR4-mediated macrophage activation contributes to reduced GSIS in type 2 diabetes and suggest that reactivating islet macrophage FFAR4 and promoting or mimicking IL-6 release from islet macrophages improves GSIS in type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metallothionein 1 negatively regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and is differentially expressed in conditions of beta cell compensation and failure in mice and humans.Diabetologia. 2019 Dec;62(12):2273-2286. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05008-3. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31624901
-
Free fatty acid receptor 4 inhibitory signaling in delta cells regulates islet hormone secretion in mice.Mol Metab. 2021 Mar;45:101166. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101166. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33484949 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 is required for the obesity-induced pancreatic beta cell dysfunction.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013 Dec;45(12):1030-8. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt092. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013. PMID: 23985305
-
20-HETE promotes glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in an autocrine manner through FFAR1.Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 12;9(1):177. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02539-4. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29330456 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological potential of novel agonists for FFAR4 on islet and enteroendocrine cell function and glucose homeostasis.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Jan 15;142:105104. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105104. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 31669388
Cited by
-
Effect of 8-Methyl Nonanoic Acid, a Degradation By-Product of Dihydrocapsaicin, on Energy and Glucose Homeostasis in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.J Exp Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 13;17:555-570. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S536185. eCollection 2025. J Exp Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40827132 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic Acid Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis via FFAR4-Mediated Regulation of Inflammatory Cytokines.Molecules. 2025 Jul 29;30(15):3180. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153180. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807354 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rorsman, P. & Braun, M. Regulation of insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Annu. Rev. Physiol75, 155–179 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

