Hyperinflammatory repolarisation of ovarian cancer patient macrophages by anti-tumour IgE antibody, MOv18, restricts an immunosuppressive macrophage:Treg cell interaction
- PMID: 40210642
- PMCID: PMC11985905
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57870-y
Hyperinflammatory repolarisation of ovarian cancer patient macrophages by anti-tumour IgE antibody, MOv18, restricts an immunosuppressive macrophage:Treg cell interaction
Abstract
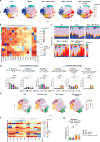
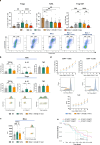
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynaecological cancer and treatment options remain limited. In a recent first-in-class Phase I trial, the monoclonal IgE antibody MOv18, specific for the tumour-associated antigen Folate Receptor-α, was well-tolerated and preliminary anti-tumoural activity observed. Pre-clinical studies identified macrophages as mediators of tumour restriction and pro-inflammatory activation by IgE. However, the mechanisms of IgE-mediated modulation of macrophages and downstream tumour immunity in human cancer remain unclear. Here we study macrophages from patients with epithelial ovarian cancers naive to IgE therapy. High-dimensional flow cytometry and RNA-seq demonstrate immunosuppressive, FcεR-expressing macrophage phenotypes. Ex vivo co-cultures and RNA-seq interaction analyses reveal immunosuppressive associations between patient-derived macrophages and regulatory T (Treg) cells. MOv18 IgE-engaged patient-derived macrophages undergo pro-inflammatory repolarisation ex vivo and display induction of a hyperinflammatory, T cell-stimulatory subset. IgE reverses macrophage-promoted Treg cell induction to increase CD8+ T cell expansion, a signature associated with improved patient prognosis. On-treatment tumours from the MOv18 IgE Phase I trial show evidence of this IgE-driven immune signature, with increased CD68+ and CD3+ cell infiltration. We demonstrate that IgE induces hyperinflammatory repolarised states of patient-derived macrophages to inhibit Treg cell immunosuppression. These processes may collectively promote immune activation in ovarian cancer patients receiving IgE therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.N.K. and J.S. are founders and shareholders of Epsilogen Ltd. S.N.K., J.S, D.H.J., G.P. and H.J.B. declare patents on antibody technologies. H.J.B., M.G. and L.P. are funded and J.L-A. was funded via a research grant by Epsilogen Ltd. A.G., S.J. and L.M. have financial interests in SeromYx Systems. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

