Pre-trained molecular representations enable antimicrobial discovery
- PMID: 40210659
- PMCID: PMC11986102
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58804-4
Pre-trained molecular representations enable antimicrobial discovery
Abstract
The rise in antimicrobial resistance poses a worldwide threat, reducing the efficacy of common antibiotics. Determining the antimicrobial activity of new chemical compounds through experimental methods remains time-consuming and costly. While compound-centric deep learning models promise to accelerate this search and prioritization process, current strategies require large amounts of custom training data. Here, we introduce a lightweight computational strategy for antimicrobial discovery that builds on MolE (Molecular representation through redundancy reduced Embedding), a self-supervised deep learning framework that leverages unlabeled chemical structures to learn task-independent molecular representations. By combining MolE representation learning with available, experimentally validated compound-bacteria activity data, we design a general predictive model that enables assessing compounds with respect to their antimicrobial potential. Our model correctly identifies recent growth-inhibitory compounds that are structurally distinct from current antibiotics. Using this approach, we discover de novo, and experimentally confirm, three human-targeted drugs as growth inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus. This framework offers a viable, cost-effective strategy to accelerate antibiotic discovery.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
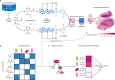

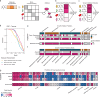

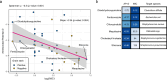

References
-
- Tommasi, R., Brown, D. G., Walkup, G. K., Manchester, J. I. & Miller, A. A. Eskapeing the labyrinth of antibacterial discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.14, 529–542 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Pandey, M. et al. The transformational role of gpu computing and deep learning in drug discovery. Nat. Mach. Intell.4, 211–221 (2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

