The gut microbiota metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide promotes cardiac hypertrophy by activating the autophagic degradation of SERCA2a
- PMID: 40210720
- PMCID: PMC11986001
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08016-9
The gut microbiota metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide promotes cardiac hypertrophy by activating the autophagic degradation of SERCA2a
Abstract
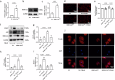
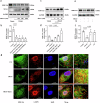
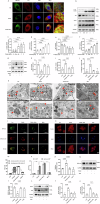
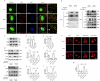
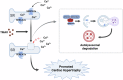
Trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) is a newly found intestinal microbiota metabolite. Here, we aimed to explore the effects of TMAO on calcium homeostasis and its implication in cardiac hypertrophy, especially focusing on the regulatory mechanism of TMAO on the key calcium transporter SERCA2a. Echocardiography and histological assessment showed that mice fed with TMAO or Choline for 8 weeks exhibited significant pathological changes of cardiac hypertrophy, which is accompanied by increased plasma levels of TMAO. The results indicated that TMAO could increase the intracellular Ca2+ level, up-regulate the expression of ANP and MYH7, and down-regulate SERCA2a expression, which could be reversed by overexpressing of SERCA2a and BAPTA-AM. Meanwhile, TMAO treatment promotes autophagy in vitro and in vivo. By employing immunofluorescence staining and immunoprecipitation assay, it was found that SERCA2a bound to ATG5 and transported to autophagosomes via the ATG5 complex for degradation under TMAO conditions. Furthermore, either 3MA or siATG5 could ameliorate TMAO-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and SERCA2a degradation. Finally, in vivo intervention showed that 3MA could relieve cardiac hypertrophy and rescue the down-regulation of SERCA2a in TMAO-fed mice. The current study identifies a mechanism in which TMAO promotes cardiac hypertrophy via elevated intracellular Ca2+ levels and enhanced autophagy degradation of SERCA2a.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gut microbe-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis.Lab Invest. 2019 Mar;99(3):346-357. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0091-y. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Lab Invest. 2019. PMID: 30068915
-
Protective Role of (-)-Epicatechin on Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy via SP1/SIRT1/SUMO1 Signaling Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Dec;24(12):1335-1347. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09932-8. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39419946 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbe-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide accelerates fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation and induces cardiac fibrosis.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019 Sep;134:119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.07.004. Epub 2019 Jul 9. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31299216
-
MicroRNA-328 as a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy.Int J Cardiol. 2014 May 1;173(2):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.02.035. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24631114
-
The cardiac sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase: a potent target for cardiovascular diseases.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008 Sep;5(9):554-65. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio1301. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008. PMID: 18665137 Review.
Cited by
-
The Non-Traditional Cardiovascular Culprits in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral Imbalance and Uremic Toxin Accumulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 17;26(16):7938. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167938. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869261 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jama, H. A., Beale, A., Shihata, W. A. & Marques, F. Z. The effect of diet on hypertensive pathology: is there a link via gut microbiota-driven immunometabolism? Cardiovascular research 115, 1435-1447, 10.1093/cvr/cvz091 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Naqvi, S. et al. A cross-talk between gut microbiome, salt and hypertension. Biomedicine Pharmacother. = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie134, (2021). 111156. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

