Circulating extracellular vesicles protein expression for early prediction of platinum-resistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
- PMID: 40210758
- PMCID: PMC12015105
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-025-03382-4
Circulating extracellular vesicles protein expression for early prediction of platinum-resistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
Abstract
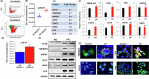
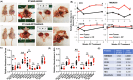
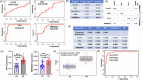
Platinum resistance in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) portends a poor prognosis. Although initial platinum-based chemotherapy response rates are high, 15-20% of patients demonstrate primary resistance to platinum therapy and almost all patients will develop platinum resistance in the recurrent setting. No predictive or diagnostic biomarkers have been utilized specific to platinum resistance. This study aimed to identify candidate biomarkers for platinum resistance in HGSOC using an extracellular vesicle (EV) based approach. We found differentially expressed and distinct EV proteins, namely TMEM205 and CFH, in patients with platinum-resistant (PR) HGSOC compared to those of platinum-sensitive (PS) patients, utilizing liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Expression of these EV proteins were validated in patient-derived PR cell lines as well as in clinically relevant mouse models of HGSOC post-platinum therapy. We corroborated these findings using serum samples from patients with PS and PR-HGSOC. Both EV CFH and EV TMEM205 exhibited excellent diagnostic capability for PR as noted by receiver operating characteristic curves with area under the curve values of 0.95 and 0.84, respectively. The high diagnostic performance of TMEM205 and CFH within EVs compared to the relatively poor performance of conventional serum proteins such as Ca125 suggests their robust potential as non-invasive biomarkers for detecting platinum resistance in HGSOC. Furthermore, the ROC curve for the combined biomarker demonstrated excellent diagnostic performance, with an AUC of 0.973, a true positive rate (TPR) of 0.938, and a false positive rate (FPR) of 0.062. Incorporating this multi-protein biomarker panel alongside established biomarkers further enhances diagnostic accuracy. Serum EV CFH and TMEM205 are promising biomarkers for early detection of platinum resistance in HGSOC and may highlight underlying chemoresistance mechanisms, offering potential future therapeutic targets.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures used in this study were authorized and conducted according to the guidelines of the Ohio State University Research Institute Ethics Committee. All animal experiments were following the Animal Experimentation Ethics of the Ohio State University Animal Experimentation Research Lab, and the ethics approval number for animal experimentation was 2012A00000008-R3. The use of stored human tissues in this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center under Study Number: 2004C0124 and the Ohio State University’s OHRP Federal wide Assurance #00006378. No human subjects were directly consented for this study as the tissues were obtained from a biorepository.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Salminen L, Nadeem N, Jain S, Grenman S, Carpen O, Hietanen S, et al. A longitudinal analysis of CA125 glycoforms in the monitoring and follow up of high grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2020;156:689–94. - PubMed
-
- Sroczynski G, Gogollari A, Kuehne F, Hallsson LR, Widschwendter M, Pashayan N, et al. A systematic review on cost-effectiveness studies evaluating ovarian cancer early detection and prevention strategies. Cancer Prev Res. 2020;13:429–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

