Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles from EGFR mutated lung cancer cells
- PMID: 40210802
- PMCID: PMC11985682
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-025-01643-w
Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles from EGFR mutated lung cancer cells
Abstract
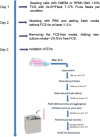
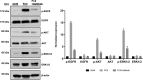
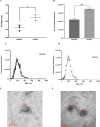
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway is essential for cellular processes such as proliferation, survival, and migration. Dysregulation of EGFR signaling is frequently observed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and is associated with poor prognosis. This study aims to isolate and characterize extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by mutant EGFR lung cancer cell line PC9 and compare them with wild-type EGFR lung cancer cell line A549, while also evaluating the effect of gefitinib treatment on EV secretion and cargo composition. The two lung cancer cell lines were cultured with 2% EV-free serum, and EVs were subsequently isolated by differential ultra centrifugation. EVs were characterized by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for quantification size and shape determination. Western blot analysis confirmed the enrichment and purity of isolated EVs. Results showed that EGFR mutation significantly increased EV release and altered their size, compared to EVs released by wild-type EGFR cells. In addition to classical EV markers such as CD81, Flotillin- 1, and TSG101, Western blot analysis also detected phosphorylated EGFR (p-EGFR) selectively packaged into EVs from PC9 cells. Gefitinib treatment significantly reduced EV secretion in PC9 cells and led to a marked decrease in p-EGFR incorporation into EVs, indicating that EV biogenesis and compostion are modulated by active EGFR signaling. In conclusion, this study highlights the significant influence of EGFR activation on EV secretion and cargo composition while demonstrating that EGFR inhibition via gefitinib alters EV-mediated signaling in lung cancer cells. These findings provide insights into tumor behavior, EV-mediated oncogenic communication, and the potential use of EVs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR; Extracellular vesicles; Lung cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose Ethical approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the amended Declaration of Helsinki and the study was approved by the institutional ethics committee of the University of Foggia (institutional review board approval number DDG N. 651 OF 27.08.2024).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of gefitinib treatment on cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells.Int J Pharm. 2019 Dec 15;572:118762. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118762. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31610280 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoplasmonic Detection of EGFR Mutations Based on Extracellular Vesicle-Derived EGFR-Drug Interaction.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Feb 21;16(7):8266-8274. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c14907. Epub 2024 Feb 9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38335730
-
Clathrin-mediated EGFR endocytosis as a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming primary resistance of EGFR TKI in wild-type EGFR non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2021 Jan;10(1):372-385. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3635. Epub 2020 Dec 12. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33314735 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3(3):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33734432 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated technologies for molecular profiling of genetic and modified biomarkers in extracellular vesicles.Lab Chip. 2025 May 28;25(11):2504-2520. doi: 10.1039/d5lc00053j. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 40135945 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicle-associated epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential liquid biopsy biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma: a case-control study.J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2025;42:36. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2025.42.36. Epub 2025 May 23. J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40414258 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin inhibits IFN-γ induced PD-L1 expression via reduction of STAT1 Phosphorylation in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells.Saudi Pharm J. 2025 Jun 5;33(3):16. doi: 10.1007/s44446-025-00018-2. Saudi Pharm J. 2025. PMID: 40471501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El Andaloussi S, Mäger I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJA. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(5):347–57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

