A reference database enabling in-depth proteome and PTM analysis of mouse immune cells
- PMID: 40210874
- PMCID: PMC11986169
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-04829-9
A reference database enabling in-depth proteome and PTM analysis of mouse immune cells
Abstract
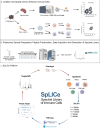
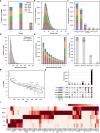
Spectral libraries fulfill multiple functions in biological and analytical applications. For biologists, these libraries provide a valuable resource to verify the presence and abundance of proteins or pathways within a selected cell type thus determine the feasibility of further experiments. Despite advances, existing libraries are incomplete and provide researchers only a limited amount of information. To address this, we introduce the reference database - Spectral Library of Immune Cells (SpLICe), a resource covering B-cells, CD4 and CD8 T-cells, macrophages and dendritic cells containing nearly 9,000 protein groups and 110,346 proteotypic peptides. Additionally, the database provides data on > 20,000 post-translationally modified proteotypic peptides (oxidation, phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, deamidation and N-glycosylation) across the selected immune cell populations. SpLICe supports the quantification of more than half of total murine proteins annotated by UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, enabling monitoring of selected proteins or pathways from Reactome pathways and Gene Ontology databases. The platform provides relative protein abundances and supports the generation of targeted mass spectrometry assays by identifying and scoring proteotypic peptides.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Generation of a murine SWATH-MS spectral library to quantify more than 11,000 proteins.Sci Data. 2020 Mar 26;7(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0449-z. Sci Data. 2020. PMID: 32218446 Free PMC article.
-
Annotation of glycoproteins in the SWISS-PROT database.Proteomics. 2001 Feb;1(2):262-8. doi: 10.1002/1615-9861(200102)1:2<262::AID-PROT262>3.0.CO;2-#. Proteomics. 2001. PMID: 11680872
-
[Size exclusion-reverse liquid column chromatography-mass spectrometry and its application in the identification of post-translationally modified proteins in rat kidney].Se Pu. 2021 Jan;39(1):87-95. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.05028. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227362 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Identification, Quantification, and Site Localization of Protein Posttranslational Modifications via Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;919:345-382. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41448-5_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27975226 Review.
-
Advances in enrichment methods for mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis of post-translational modifications.J Chromatogr A. 2022 Aug 16;1678:463352. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463352. Epub 2022 Jul 19. J Chromatogr A. 2022. PMID: 35896048 Review.
References
-
- Awasthi, K. et al. Data-independent acquisition approach to proteome: A case study and a spectral library for mass spectrometry-based investigation of mycobacterium tuberculosis. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology26, 142–150 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FOR5427 SP1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- INST 337/15-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- INST 337/15-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- FOR5427 SP4; EN984/15-1, 16-1 and 18-1; TR296 P09; TR332 A3 and Z1; INST 20876/486-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

