A real-world descriptive study of screening practices for hydroxychloroquine retinopathy in Japan using an insurance claims database
- PMID: 40210937
- PMCID: PMC11985982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96579-2
A real-world descriptive study of screening practices for hydroxychloroquine retinopathy in Japan using an insurance claims database
Abstract
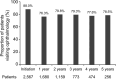
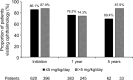
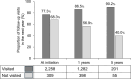
Since 2015, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has been widely used as a standard treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) under the national health insurance system in Japan. However, the status of routine ophthalmological screening for retinopathy, which is a notable safety concern of HCQ, remains unclear. In this retrospective study using the nationwide health insurance claims database, we aimed to investigate the status of ophthalmological screening in routine clinical practice in Japan. A total of 2567 patients with SLE or CLE were included in the analysis. The proportion of ophthalmology visits was 88.0% at the initiation of HCQ prescription, decreased to 76.3% after one year, and then remained constant. Moreover, only 50% of the patients underwent spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and automated visual field (VF) tests, which are useful for the early detection of HCQ retinopathy-related changes. Importantly, the proportion of ophthalmology visits remained consistently high among patients who visited an ophthalmologist in the previous year, ranging from 77.3% to 90.2%. These findings highlight the need to improve screening adherence and promote regular ophthalmological evaluations, particularly for patients without prior ophthalmology visits, to enhance the early detection of HCQ retinopathy.
Keywords: Hydroxychloroquine; Lupus erythematosus; Ophthalmological screening; Retinopathy; Safety.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Kumiko Kato declares no competing interests; Mineo Kondo declares no competing interests; Kei Shinoda declares no competing interests; Naoto Yokogawa declares receiving speaker fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation; Takumi Tajima is an employee of JMDC, Inc.; and Toshiya Takahashi is an employee of Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation. Ethical approval: The data source for this study was an anonymized, de-identified/de-linked secondary database that was used only for research purposes by the database vendor and was not linked to individual patient medical records. The requirement for informed consent was waived, and an opt-out approach was applied in compliance with local regulations. The study adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was not obtained because local regulations do not require it for studies utilizing pre-existing anonymized, de-identified/de-linked databases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk factors for hydroxychloroquine retinopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study with hydroxychloroquine blood-level analysis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Dec 1;59(12):3807-3816. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa157. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32442312 Free PMC article.
-
Nationwide patterns of hydroxychloroquine dosing and monitoring of retinal toxicity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Sci Rep. 2023 May 4;13(1):7270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34022-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37142639 Free PMC article.
-
Current screening practice in patients under long-term hydroxychloroquine medication in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(14):e15122. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015122. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30946384 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrochloroquine retinopathy: characteristic presentation with review of screening.Clin Rheumatol. 2013 Jun;32(6):895-8. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2226-2. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Clin Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23515601 Review.
-
Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Mar;16(3):411-419. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1269168. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 27927040 Review.
References
-
- Guidelines for referral and management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Guidelines. Arthritis Rheum.42, 1785–1796 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Marmor, M. F., Kellner, U., Lai, T. Y., Melles, R. B. & Mieler, W. F.; American Academy of Ophthalmology. Recommendations on screening for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine retinopathy (2016 revision). Ophthalmology123, 1386–1394 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Fanouriakis, A. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis.83, 15–29 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Yokogawa, N. et al. Effects of hydroxychloroquine in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus: A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheumatol.69, 791–799 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Marmor, M. F. & Hu, J. Effect of disease stage on progression of hydroxychloroquine retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol.132, 1105–1112 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

