HTS analysis of resistance induction against PPV by four hairpin constructs in Nicotiana benthamiana Domin
- PMID: 40210976
- PMCID: PMC11985976
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97546-7
HTS analysis of resistance induction against PPV by four hairpin constructs in Nicotiana benthamiana Domin
Abstract
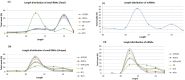
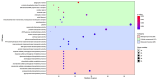
Plum pox virus (PPV) is the most devastating viral disease of the stone fruits worldwide. Inefficiency of the traditional control measures against PPV along with its globally widespread distribution and the economic importance of stone fruits, signify the necessity and importance of PPV resistance programs. In the present study, Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Nicotiana benthamiana Domin was performed using four inverted repeat constructs derived from UTR/P1, HCPro, HCPro/P3, and CP regions of PPV-T isolate KyEsAp301. The efficacy of the constructs for inducing virus resistance in transgenic plants was evaluated by inoculation with PPV-D, -M, and -T strains. The potential of hairpin structures in the production of siRNAs and miRNAs in both wild-type and transgenic plants was compared by small RNA high-throughput sequencing. Although the four PPV genomic regions were used for transgenic resistance in previous experiments, small RNA high-throughput sequencing was first time used in this study to demonstrate the efficacy of the PPV constructs and to determine expression profiles of siRNAs and miRNAs. The results revealed that the potentials of hairpin constructs in producing siRNAs and their accumulation in target regions were significantly different. Expression profiles of several known and novel miRNAs were dramatically changed in response to PPV infection in both wild-type and transgenic plants, demonstrating plausible involvement of these miRNAs in plant-virus interactions. Based on the abundance of siRNAs and lack of PPV virus accumulation in transgenic plants harboring UTR/P1 and CP hairpin construct, we have concluded that UTR/P1 and CP are likely the best viral regions for induction of resistance against PPV.
Keywords: Potyvirus; RNAi; Small RNA sequencing; Virus silencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Statement specifying permissions: For this study, we acquired permission to study Nicotiana benthamiana issued by the Agricultural and Forestry Ministry of Türkiye. Statement on experimental research and field studies on plants: The either cultivated or wild-growing plants sampled comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and domestic legislation of Türkiye.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hairpin RNA-mediated silencing of Plum pox virus P1 and HC-Pro genes for efficient and predictable resistance to the virus.Transgenic Res. 2005 Dec;14(6):989-94. doi: 10.1007/s11248-005-1773-y. Transgenic Res. 2005. PMID: 16315100
-
Silencing of Plum pox virus 5'UTR/P1 sequence confers resistance to a wide range of PPV strains.Plant Cell Rep. 2010 Dec;29(12):1435-44. doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0933-6. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Plant Cell Rep. 2010. PMID: 20963442
-
Differential RNAi responses of Nicotiana benthamiana individuals transformed with a hairpin-inducing construct during Plum pox virus challenge.Virus Genes. 2014 Oct;49(2):325-38. doi: 10.1007/s11262-014-1093-5. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Virus Genes. 2014. PMID: 24964777
-
The use of transgenic fruit trees as a resistance strategy for virus epidemics: the plum pox (sharka) model.Virus Res. 2000 Nov;71(1-2):63-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(00)00188-x. Virus Res. 2000. PMID: 11137162 Review.
-
Genetically engineered resistance to Plum pox virus infection in herbaceous and stone fruit hosts.GM Crops. 2011 Jan-Mar;2(1):24-33. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.2.1.15096. GM Crops. 2011. PMID: 21844696 Review.
References
-
- Schmelzer, K. Zier-, Forst-und Wildgehölze. Pflanzliche Virologie 276–405 (Akademie, 1977).
-
- Garcia, J. A. & Cambra, M. Plum pox virus and Sharka disease. Plant. Viruses. 1 (1), 69–79 (2007).
-
- Moreno, A., Fereres, A. & Cambra, M. Quantitative Estimation of Plum pox virus targets acquired and transmitted by a single Myzus persicae. Arch. Virol.154, 1391–1399. 10.1007/s00705-009-0450-5 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe, D. RNA Silencing in plants. Nature431 (7006), 356–363. 10.1038/nature02874 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

