SOX9-dependent fibrosis drives renal function in nephronophthisis
- PMID: 40211043
- PMCID: PMC12162883
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00233-3
SOX9-dependent fibrosis drives renal function in nephronophthisis
Abstract
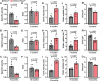
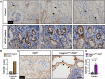
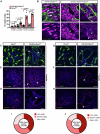
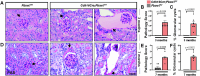
Fibrosis is a key feature of a broad spectrum of cystic kidney diseases, especially autosomal recessive kidney disorders such as nephronophthisis (NPHP). However, its contribution to kidney function decline and the underlying molecular mechanism(s) remains unclear. Here, we show that kidney-specific deletion of Fbxw7, the recognition receptor of the SCFFBW7 E3 ubiquitin ligase, results in a juvenile-adult NPHP-like pathology characterized by slow-progressing corticomedullary cysts, tubular degeneration, severe fibrosis, and gradual loss of kidney function. Expression levels of SOX9, a known substrate of FBW7, and WNT4, a potent pro-fibrotic factor and downstream effector of SOX9, were elevated upon loss of FBW7. Heterozygous deletion of Sox9 in compound mutant mice led to the normalization of WNT4 levels, reduced fibrosis, and preservation of kidney function without significant effects on cystic dilatation and tubular degeneration. These data suggest that FBW7-SOX9-WNT4-induced fibrosis drives kidney function decline in NPHP and, possibly, other forms of autosomal recessive kidney disorders.
Keywords: FBW7; Fibrosis; Kidney Function; Nephronophthisis; SOX9.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ala-Mello S, Kivivuori SM, Ronnholm KA, Koskimies O, Siimes MA (1996) Mechanism underlying early anaemia in children with familial juvenile nephronophthisis. Pediatr Nephrol 10:578–581 - PubMed
-
- Attanasio M, Uhlenhaut NH, Sousa VH, O’Toole JF, Otto E, Anlag K, Klugmann C, Treier AC, Helou J, Sayer JA et al (2007) Loss of GLIS2 causes nephronophthisis in humans and mice by increased apoptosis and fibrosis. Nat Genet 39:1018–1024 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/Y007808/1/UKRI | Medical Research Council (MRC)
- DK126705/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- 20180925/Kidney Research UK
- P30 CA225520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK119375/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- R01 DK126705/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK138339/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK119375/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- LifeArc Pathfinder 1.0/LifeArc
- P20 GM103639/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK129255/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK138339/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- DK129255/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- R24 GM137786/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

