Repression of ZNFX1 by LncRNA ZFAS1 mediates tobacco-induced pulmonary carcinogenesis
- PMID: 40211119
- PMCID: PMC11983736
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-025-00705-x
Repression of ZNFX1 by LncRNA ZFAS1 mediates tobacco-induced pulmonary carcinogenesis
Abstract
Background: Despite exhaustive research efforts, integrated genetic and epigenetic mechanisms contributing to tobacco-induced initiation and progression of lung cancers have yet to be fully elucidated. In particular, limited information is available regarding dysregulation of noncoding RNAs during pulmonary carcinogenesis.
Methods: We examined correlations and interactions of long noncoding (lnc) RNAs and protein-coding genes in normal respiratory epithelial cells (NREC) and pulmonary tumor cells following exposure to cigarette smoke condensate (CSC) using gene expression arrays, qRT-PCR, western blot, growth assays, transwell assays, and murine xenograft models, as well as methylated DNA immunoprecipitation, RNA cross-link immunoprecipitation, and quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation techniques with bioinformatics analyses.
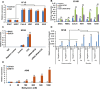
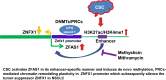
Results: Among diverse alterations of lncRNA and coding gene expression profiles in NREC exposed to CSC, we observed upregulation of lncRNA ZFAS1 and repression of an adjacent protein-coding gene, ZNFX1, and confirmed these findings in primary lung cancers. Phenotypic experiments indicated that ZFAS1 is an oncogene, whereas ZNFX1 functions as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer cells. Mechanistically, CSC induces ZFAS1 expression via SP1 and NFĸB-associated activation of an enhancer linked to ZFAS1. Subsequently, ZFAS1 interacts with DNA methyltransferases and polycomb group proteins to silence ZNFX1. Mithramycin and methysticin repress ZFAS1 and upregulate ZNFX1 in lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: These studies reveal a novel feedforward lncRNA circuit contributing to pulmonary carcinogenesis and suggest that pharmacologic targeting of SP1 and/or NFĸB may be useful strategies for restoring ZNFX1 expression for lung tumor therapy.
Keywords: ZFAS1; ZNFX1; BMI1; Cigarette smoke; DNMT; EZH2; Epigenetics; Lung cancer; NFĸB; Noncoding RNA; SP1; SUZ12.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the NIH internal review board (approval no. 06C0014; date: 02/28/2023) based on the Helsinki Declaration. All animal experiments were approved by the National Cancer Institute Animal Care and Use Committee (approval no. SB-200; date: 07/03/2024) and were performed according to international guidelines and the Basel Declaration. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 24;9(10):982. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0962-6. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30250022 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA ZNFX1-AS1 promotes the tumor progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-144 to regulate EZH2 expression.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Feb 15;10(3):150. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1332-8. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30770796 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via targeting miR-10a/SKA1 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Mar;111:917-925. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.143. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30841471
-
ZFAS1: A novel vital oncogenic lncRNA in multiple human cancers.Cell Prolif. 2019 Jan;52(1):e12513. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12513. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30288832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA ZFAS1: Role in tumorigenesis and other diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Oct;142:111999. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111999. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34385106 Review.
References
-
- Leiter A, Veluswamy RR, Wisnivesky JP. The global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends. Nature Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20:624–39. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–63. - PubMed
-
- Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF, Heist RS. Lung cancer. Lancet. 2021;398:535–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

