Improvement in postoperative pain control by combined use of intravenous dexamethasone with dexmedetomidine after erector spinae plane block and serratus anterior plane block for thoracoscopic surgery: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40211141
- PMCID: PMC11984028
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-025-03039-5
Improvement in postoperative pain control by combined use of intravenous dexamethasone with dexmedetomidine after erector spinae plane block and serratus anterior plane block for thoracoscopic surgery: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acute pain after thoracoscopic surgery is very noticeable and often requires additional techniques or adjunctive medications to reduce it. We investigated whether intravenous dexamethasone with dexmedetomidine after erector spinae plane block and serratus anterior plane block could further decrease the incidence of moderate-to-severe pain.
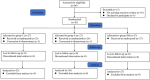
Methods: A total of 81 patients were randomly assigned to group C (20 mL normal saline), group S (10 mg dexamethasone + normal saline to 20 mL), or group SM (10 mg dexamethasone + 1 µg/kg dexmedetomidine + normal saline to 20 mL). All patients underwent erector spinae plane block and serratus anterior plane block 30 min before anesthesia induction and all drugs were infused intravenously 30 min after general anesthesia induction. The primary outcome was incidence of moderate-to-severe pain at 24 h on movement postoperatively. Secondary outcomes included incidence of moderate-to-severe pain on movement and at rest throughout the first two postoperative days, pain score, opioid consumption, quality of recovery and adverse effects.
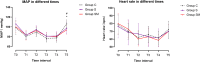
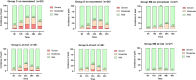
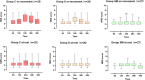
Results: Group SM lowered the incidence of moderate-to-severe pain on movement at 24 h postoperatively than group C (11.1% vs. 48.0%; RR 0.231; 95% CI, 0.074 to 0.725) and group S (11.1% vs. 38.5%; RR 0.289; 95% CI, 0.089 to 0.933). Group SM reduced NRS score on movement (3.0 [3.0] vs. 3.0 [2.0] vs. 3.0[1.0]; P < 0.001) and total opioid consumption (26.0 [6.0] vs. 32.0 [9.0] vs. 28.0 [2.5]; P = 0.004) within 24 h after surgery, fewer patients required rescue analgesia (11.1% vs. 48.0% vs. 38.5%; P = 0.009). Group SM also lowered incidence of nausea and vomiting (7.4% vs. 32.0% vs. 30.8%; P = 0.047) and had a higher QoR-15 score at postoperative 24 h (132.0 [10.0] vs. 123.0 [8.0] vs. 127.5 [10.8]; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Intravenous administration of dexamethasone with dexmedetomidine after erector spinae plane block and serratus anterior plane block further decreased the incidence of moderate-to-severe pain. It also reduced NRS scores and opioid consumption, making the postoperative pain control better for thoracoscopic surgery.
Trial registration: The study was registered at Chictr.org.cn with the number ChiCTR2400084435 on 05/16/2024.
Keywords: Analgesia; Dexamethasone; Dexmedetomidine; Fascial plane block; Thoracoscopic surgery.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This is a double-blind, prospective randomized controlled trial conducted from May 16, 2024 to July 31, 2024 at the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University (XYFY2024-KL193-01) and was registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2400084435; registration date: May 16, 2024). All subjects were provided with written informed consent to participate in this study and all experiments were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. CONSORT guidelines: Our study fully adhered to CONSORT guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- Feray S, Lubach J, Joshi GP, Bonnet F, Van de Velde M, PROSPECT Working Group *of the European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy. PROSPECT guidelines for video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: a systematic review and procedure-specific postoperative pain management recommendations. Anaesthesia. 2022;77(3):311–25. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

