Exploring Retene's Tumour-Initiating Potential: Integrating Computational and Experimental Approaches
- PMID: 40211435
- PMCID: PMC11985699
- DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.70034
Exploring Retene's Tumour-Initiating Potential: Integrating Computational and Experimental Approaches
Keywords: Swiss albino mice; bioinformatic tools; carcinogenicity; chemical skin‐carcinogenesis; retene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
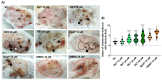
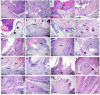
References
-
- da Silva Junior F. C., Felipe M. B. M. C., de Castro D. E. F., da Silva Araújo S. C., Sisenando H. C. N., and de Medeiros S. R. B., “A Look Beyond the Priority: A Systematic Review of the Genotoxic, Mutagenic, and Carcinogenic Endpoints of Non‐Priority PAHs,” Environmental Pollution 278 (2021): 116838, 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116838. - DOI - PubMed
-
- O’Malley K. E., Ghetu C. C., Rohlman D., and Anderson K. A.. 2024. “Assessing Wildfire Impact on Diffusive Flux of Parent and Alkylated PAHs: A Pilot Study of Soil–Air Chemical Movement before, during, and after Wildfires,” Environmental Science & Technology 58, no. 52: 23117–23126, 10.1021/acs.est.4c09139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chung E., Russo D. P., Ciallella H. L., et al., “Data‐Driven Quantitative Structure‐Activity Relationship Modeling for Human Carcinogenicity by Chronic Oral Exposure,” Environmental Science & Technology 57 (2023): 6573–6588, 10.1021/ACS.EST.3C00648/ASSET/IMAGES/MEDIUM/ES3C00648_0010.GIF. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

