Association between chronic kidney disease severity and retinopathy in hypertensive, diabetic, and mixed retinopathy in Nepal: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40212211
- PMCID: PMC11981297
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003090
Association between chronic kidney disease severity and retinopathy in hypertensive, diabetic, and mixed retinopathy in Nepal: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Introduction: Hypertensive, diabetic, and mixed retinopathies are prevalent ocular conditions that can serve as indicators of systemic diseases, particularly chronic kidney disease (CKD). The association between the severity of these retinopathies and the grading of CKD remains under-explored. This study aims to elucidate the correlation between the severity of hypertensive, diabetic, or mixed retinopathies and the stages of CKD, providing insights into the interconnected pathophysiology of these conditions.
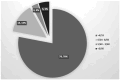
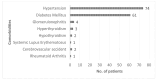
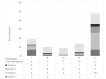
Methodology: A cross-sectional study was conducted involving 100 patients diagnosed with hypertensive, diabetic, or mixed retinopathies. Participants were categorized based on their retinopathy type and severity using standardized grading systems. CKD staging was determined according to the kidney disease guidelines. Data were collected through comprehensive ophthalmic examinations, retinal imaging's and patient medical histories. Statistical analysis was performed to assess the association between retinopathy severity and CKD stages using odds ratio (OR).
Results: The study found a significant positive correlation between the severity of retinopathies and the stages of CKD. Hypertensive Retinopathy with visual morbidity and complications was found to be associated with greater severity of CKD (OR = 2.98, P = 0.014). Patients with advanced CKD stages had more severe diabetic retinopathy compared to those with lesser severity with OR of 3.60 (P = 0.013). Mixed retinopathy had the strongest association with severity of CKD with OR of 9.07; P = 0.002).
Conclusion: The severity of hypertensive, diabetic, and mixed retinopathies correlates strongly with CKD progression. These findings highlight the need for integrated care models emphasizing regular ophthalmic and renal evaluations in at-risk populations. Early detection and management of retinopathies may facilitate timely intervention for CKD, reducing systemic disease burden.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; diabetes; hypertension; mixed retinopathy; retinopathy severity.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article. None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Risk factors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients with longer duration of diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 9;13:1079725. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1079725. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36568108 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertensive retinopathy and associated factors among nondiabetic chronic kidney disease patients seen at a tertiary hospital in Tanzania: a cross-sectional study.Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2019 May 1;12:79-86. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S196841. eCollection 2019. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31118738 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease Study in Diabetic Patients: Insights From Primary Care Units in Northern Portugal.Cureus. 2024 May 31;16(5):e61417. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61417. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38947587 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors for the development and progression of proliferative diabetic retinopathy in people with diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 22;2(2):CD013775. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013775.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36815723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vision Impairment in CKD Patients: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, Differential Diagnoses, and Prevention.Am J Kidney Dis. 2019 Jun;73(6):846-857. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.12.047. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019. PMID: 30929852 Review.
References
-
- Cockwell P, Fisher LA. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet [Internet] 2020;395:662–64. - PubMed
-
- Sapkota A, Sedhain A, Rai MK. Quality of life of adult clients on renal replacement therapies. 2013;39:228–35. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Hung T, Lee Y, et al. . Association between chronic kidney disease and risk of cataract: a nationwide. Am J Nephrol 2017;45:524–31. - PubMed
-
- Wong CW, Wong TY, Cheng CY, et al. . Kidney and eye diseases: common risk factors, etiological mechanisms, and pathways. Kidney Int 2014;85:1290–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
