Nanoarchitectonics Revolution and Evolution: From Small Science to Big Technology
- PMID: 40212414
- PMCID: PMC11935860
- DOI: 10.1002/smsc.202000032
Nanoarchitectonics Revolution and Evolution: From Small Science to Big Technology
Abstract
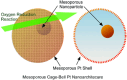
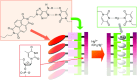
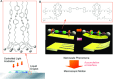
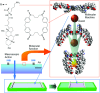
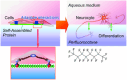
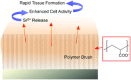
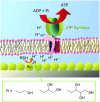
Along with the progresses of material syntheses, the importance of structural regulation is realized to rationally improve the efficiencies and specificities in target functions. Small science is necessary for advanced material systems. A novel concept, nanoarchitectonics, to combine nanotechnology with the other scientific disciplines to synthesize a functional material system with contributions of small objects, nano-units, is recently proposed. Based on facts and knowledge in nanoscale objects explored by nanotechnology, functional material systems are constructed using nano-units with the aid of the other research fields, such as organic chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, materials science, and biology. The introduction of nanoarchitectonics essences to material construction can produce unusual functional systems, such as brain-like information processing based on atomic-level reactions, diffusions, and aggregations. Probe-tip-mediated organic reactions are also possible with precise site selectivity. The coupling of equilibrium self-assemblies and non-equilibrium fabrication processes results in variously structured and hierarchical functional structures even from simple 0D nano-units such as fullerenes. Especially, interfacial nanoarchitectonics directly bridge nanoscopic functions and macroscopic actions, including facile contact with nanostructures and living cells. This review article overviews nanoarchitectonics from origin to future, from atoms to materials, and from small science to big technology.
Keywords: interfaces; living cells; molecular machines; nanoarchitectonics; nanotechnology; self-assembly.
© 2020 The Authors. Small Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Nanoarchitectonics from Molecular Units to Living-Creature-Like Motifs.Chem Rec. 2018 Jul;18(7-8):676-695. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201700070. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Chem Rec. 2018. PMID: 29205796 Review.
-
Nanoarchitectonics: what's coming next after nanotechnology?Nanoscale Horiz. 2021 May 4;6(5):364-378. doi: 10.1039/d0nh00680g. Nanoscale Horiz. 2021. PMID: 33949390
-
Molecular nanoarchitectonics: unification of nanotechnology and molecular/materials science.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2023 Apr 3;14:434-453. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.14.35. eCollection 2023. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37091285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Molecular Nanoarchitectonics and Materials Nanoarchitectonics.Molecules. 2021 Mar 15;26(6):1621. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061621. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33804013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-assembly as a key player for materials nanoarchitectonics.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2019 Jan 31;20(1):51-95. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2018.1553108. eCollection 2019. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 30787960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ionic self-assembly of redox-active polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes: mesostructured soft materials for electrochemical nanoarchitectonics.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025 Apr 29;26(1):2497309. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2025.2497309. eCollection 2025. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40458735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- a) Guo D., Shibuya R., Akiba C., Saji S., Kondo T., Nakamural J., Science 2016, 351, 361; - PubMed
- b) Maeda K., Mallouk T. E., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 38;
- c) Li B. S., Lai C., Zeng G. M., Huang D. L., Qin L., Zhang M. M., Cheng M., Liu X. G., Yi H., Zhou C. Y., Huang F. L., Liu S. Y., Fu Y. K., Small 2019, 15, 1804565; - PubMed
- d) Roy N., Suzuki N., Terashima C., Fujishima A., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 178;
- e) Chen G.-F., Ren S. Y., Zhang L. L., Cheng H., Luo Y. R., Zhu K. H., Ding L.-X., Wang H. H., Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800337;
- f) Du L., Xing L., Zhang G., Dubois M., Sun S., Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000016.
-
- a) Yu H., Jiang L., Wang H., Huang B., Yuan X., Huang J., Zhang J., Zeng G., Small 2019, 15, 1901008; - PubMed
- b) Yang Z., Asoh T., Uyama H., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 1453;
- c) Kanao E., Kubo T., Otsuka K., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 482;
- d) Guan G., Ye E., You M., Li Z., Small 2020, 16, 1907087. - PubMed
-
- a) Li B. L., Setyawati M. I., Chen L., Xie J., Ariga K., Lim C.-T., Garaj S., Leong D. T., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15286; - PubMed
- b) Jackman J. A., Ferhan A. R., Cho N.-J., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 1404;
- c) Zhang X. G., Zhang X. L., Luo C., Liu Z., Chen Y., Dong S., Jiang C., Yang S., Wang F., Xiao X., Small 2019, 15, 1805516; - PubMed
- d) Eom S., Choi G., Nakamura H., Choy J.-H., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 1;
- e) Song J., Yuan C., Jiao T., Xing R., Yang M., Adams D. J., Yan X., Small 2020, 16, 1907309; - PubMed
- f) Paris J. L., Vallet-Regí M., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 220. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Povie G., Segawa Y., Nishihara T., Miyauchi Y., Itami K., Science 2017, 356, 172; - PubMed
- b) Kawamura S., Sodeoka M., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 1245;
- c) Sun Z., Ikemoto K., Fukunaga T. M., Koretsune T., Arita R., Sato S., Isobe H., Science 2019, 363, 151; - PubMed
- d) Muramatsu W., Hattori T., Yamamoto H., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 759.
-
- a) Akagi K., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 1509;
- b) Lian J., Huang Y.-B., Cao R., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 32;
- c) Yamago S., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 287;
- d) Huang J., Huang S., Zhao Y., Feng B., Jiang K., Sun S., Ke C., Kymakis E., Zhuang X., Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000628.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
