A systematic review of proximal humerus fractures and associated vascular injuries
- PMID: 40212535
- PMCID: PMC7617580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsvi.2024.100065
A systematic review of proximal humerus fractures and associated vascular injuries
Abstract
Objective: Proximal humerus fractures are common with a reported neurovascular injury incidence of 0.09% to 5%. This study aimed to synthesize the current evidence on the presentation and management of proximal humerus fractures with associated vascular injury to aid clinical decision-making.
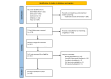
Methods: A systematic review was conducted following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (PROSPERO registration: CRD42023393957) to identify articles reporting proximal humerus fractures with associated vascular injury in adults. Study quality was assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools checklist. Outcomes included presentation, fracture classification, type of vascular injury, method of orthopedic and vascular repair, and complications.
Results: A total of 40 articles representing 55 individuals with a fracture were included. Injuries most commonly occurred after a low-energy mechanism such as a fall from a standing height (n = 32, 58%). The presentation of ischemia included cool limb (n = 29, 53%), pallor (n = 21, 38%), prolonged capillary refill (n = 7, 13%), and an absent or reduced pulse (n = 47, 85%). Concomitant neurological injury was reported in 30 cases (55%) and fracture dislocations were reported in 17 cases (32.7%). Fracture classification was variable; however, when all recorded fracture patterns were described in terms of 2-, 3-, or 4-part fractures, these represented 49% (n = 27), 24% (n = 13), and 18% (n = 10), respectively. Fracture management preceded vascular repair in 30 (55%). Orthopedic management was primarily performed by open reduction internal fixation or wire fixation (n = 33, 60%) and hemiarthroplasty (n = 11, 20%). Isolated arterial injury was the most common vascular injury (n = 52, 95%). Arterial injuries were primarily repaired by an interposition graft (n = 21, 38%), primary repair (n = 11, 20%), or conservative management (n = 9, 16%). Complications such as amputation, compartment syndrome, avascular necrosis, and metalwork failure were reported in 13 cases.
Conclusions: Proximal humerus fractures with associated vascular injuries occur most commonly in the older adults after low-energy mechanisms such as a fall from a standing height. A high index of suspicion is needed as not all injuries present with classical ischemic symptoms, and these injuries carry significant associated morbidity. (JVS-Vascular Insights 2024;2:100065.).
Keywords: Humeral fracture; Trauma; Vascular injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures None. The editors and reviewers of this article have no relevant financial relationships to disclose per the Journal policy that requires reviewers to decline review of any manuscript for which they may have a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What Factors Are Associated With Poor Shoulder Function and Serious Complications After Internal Fixation of Three-part and Four-part Proximal Humerus Fracture-dislocations?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022 Aug 1;480(8):1566-1573. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002190. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022. PMID: 35333197 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Lateral Condyle Humeral Fracture Associated With Elbow Dislocation in Children. A Retrospective International Multicenter Cohort Study.J Pediatr Orthop. 2024 Feb 1;44(2):82-88. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002574. Epub 2023 Nov 20. J Pediatr Orthop. 2024. PMID: 37982458
-
[Complex injury of the elbow joint].Unfallchirurg. 1996 Feb;99(2):92-99. Unfallchirurg. 1996. PMID: 8881223 Review. German.
-
Proximal humerus fractures: anatomy, diagnosis and management.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2022 Jul 2;83(7):1-10. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2021.0554. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35938761
-
Proximal Humerus Fractures: A Review of Anatomy, Classification, Management Strategies, and Complications.Cureus. 2024 Nov 5;16(11):e73075. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73075. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39640099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pencle FJ, Gossman WG. Proximal humerus fracture. StatPearls; 2022.
-
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37:691–697. - PubMed
-
- Rangan A, Handoll H, Brealey S, et al. Surgical vs nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: the PROFHER randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;313:1037–1047. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources