Lithium Antiperovskite-Derived Glass Solid Electrolytes
- PMID: 40212582
- PMCID: PMC11979957
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.4c02578
Lithium Antiperovskite-Derived Glass Solid Electrolytes
Abstract
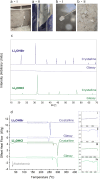
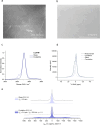
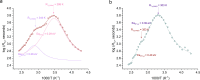
In this paper, we report the synthesis of Li2OHX (X = Br, Cl)-based glasses. These glasses were found to be challenging to synthesize, requiring extreme cooling rates achievable only by a twin-roll quench process. As has been speculated for antiperovskite-derived glasses, indications of improved lithium-ion dynamics are observed. Notably, spin-lattice relaxation nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals a higher hopping frequency and significantly lower activation energy for Li2OHBr glasses (0.29 eV) compared to the crystalline Li2OHBr (0.39 eV). This may be attributable to the increased free volume in the glass samples (ρglass/ρcryst = 0.83) and a reduced ionic interaction of lithium ions with the glass structure. Despite these promising findings, the glasses were found to be unstable under pressure and crystallized in attempts to produce bulk samples for impedance measurements.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Janek J.; Zeier W. G. A solid future for battery development. Nature Energy 2016, 1, 1–4. 10.1038/nenergy.2016.141. - DOI
-
- Manthiram A.; Yu X.; Wang S. Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes. Nature Reviews Materials 2017, 2, 1–16. 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.103. - DOI
-
- Song A. Y.; Xiao Y.; Turcheniuk K.; Upadhya P.; Ramanujapuram A.; Benson J.; Magasinski A.; Olguin M.; Meda L.; Borodin O.; Yushin G. Protons Enhance Conductivities in Lithium Halide Hydroxide/Lithium Oxyhalide Solid Electrolytes by Forming Rotating Hydroxy Groups. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1700971–1700981. 10.1002/aenm.201700971. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
