Bright Semiconductor Quantum Dots Shed New Light on Precision Nanomedicine for Various Diseases
- PMID: 40212631
- PMCID: PMC11935123
- DOI: 10.1002/smsc.202300081
Bright Semiconductor Quantum Dots Shed New Light on Precision Nanomedicine for Various Diseases
Abstract
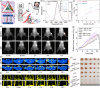
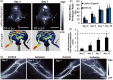
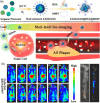
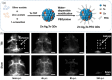
Nanomaterials with diagnostic and therapeutic functions have exciting potential to reshape the landscape of precision medicine. Impressive progress has been made toward the design and production of innovative theranostic nanomaterials that improve disease care, motivated by their ability to simultaneously provide diagnostic information and therapeutic benefits. Herein, the state-of-the-art theranostic semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) are summarized, and the diverse types of QDs designed for the diagnosis and treatment of different diseases are discussed. The opportunities and benefits of QDs are highlighted throughout using in vitro and in vivo examples aimed at addressing various clinical challenges, including cancer, vascular dysfunctions, microbial infections, and medical tattoos. Over the past several years, this area has experienced enormous growth, particularly in preclinical animal imaging and therapy, which has brought the field closer to reaching human patients. Unfortunately, several barriers to clinical translation remain. Therefore, in addition to summarizing the key results from previous in vivo studies, the lessons learned from these studies are synthesized, perspective on the future steps needed for both fundamental studies and the clinical translation of theranostic QD nanotechnology to inform future QD design is provided.
Keywords: cancer; medical tattoo; microbial infection; semiconductor quantum dots; vascular dysfunction.
© 2023 The Authors. Small Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An investigation of quantum dot theranostic probes for prostate and leukemia cancer cells using a CdZnSeS QD-based nanoformulation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Dec;675:1032-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.07.075. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 39008921
-
Quantum dots in nanomedicine: recent trends, advances and unresolved issues.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Dec 18;468(3):419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.039. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26168726 Review.
-
Multifunctional Photonic Nanomaterials for Diagnostic, Therapeutic, and Theranostic Applications.Adv Mater. 2018 Mar;30(10). doi: 10.1002/adma.201701460. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 29363198 Review.
-
Quantum dots as a theranostic approach in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2021 Aug;16(18):1595-1611. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2021-0104. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34180261
-
Quantum Dots as Theranostic Agents: Recent Advancements, Surface Modifications, and Future Applications.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(12):1257-1272. doi: 10.2174/1389557522666220405202222. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35382722
References
-
- a) Doane T. L., Burda C., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2885; - PubMed
- b) Shi J., Kantoff P. W., Wooster R., Farokhzad O. C., Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Manzari M. T., Shamay Y., Kiguchi H., Rosen N., Scaltriti M., Heller D. A., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 351; - PMC - PubMed
- d) Pelaz B., Alexiou C., Alvarez-Puebla R. A., Alves F., Andrews A. M., Ashraf S., Balogh L. P., Ballerini L., Bestetti A., Brendel C., Bosi S., Carril M., Chan W. C., Chen C., Chen X., Chen X., Cheng Z., Cui D., Du J., Dullin C., Escudero A., Feliu N., Gao M., George M., Gogotsi Y., Grunweller A., Gu Z., Halas N. J., Hampp N., Hartmann R. K., Hersam M. C., et al., ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2313; - PMC - PubMed
- e) Huang Y., Ren J., Qu X., Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357; - PubMed
- f) Sahay G., Alakhova D. Y., Kabanov A. V., J. Control Release 2010, 145, 182. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Durymanov M., Kamaletdinova T., Lehmann S. E., Reineke J., J. Control Release 2017, 261, 10; - PubMed
- b) Zhang P. S., Li Y. Y., Tang W., Zhao J., Jing L. H., McHugh K. J., Nano Today 2022, 42, 101335;
- c) Wheeler T. T., Cao P., Ghouri M. D., Ji T., Nie G., Zhao Y., Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 1498;
- d) Liu Q., Cheng H.-B., Ma R., Yu M., Huang Y., Li L., Zhao J., Nano Today 2023, 48, 101747;
- e) Yang B., Chen Y., Shi J., Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881; - PubMed
- f) Zhang P., Meng J., Li Y., Yang C., Hou Y., Tang W., McHugh K. J., Jing L., Innovation 2021, 2, 100174. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Bjornmalm M., Thurecht K. J., Michael M., Scott A. M., Caruso F., ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9594; - PubMed
- b) Greish K., Mathur A., Bakhiet M., Taurin S., Ther. Delivery 2018, 9, 269; - PubMed
- c) Ren J., Andrikopoulos N., Velonia K., Tang H., Cai R., Ding F., Ke P. C., Chen C., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9184; - PubMed
- d) Kabanov A. V., Adv. Drug Delivery. Rev. 2006, 58, 1597. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Jing L., Kershaw S. V., Li Y., Huang X., Li Y., Rogach A. L., Gao M., Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10623; - PubMed
- b) Lesyuk R., Lesnyak V., Herguth A., Popovych D., Bobitski Y., Klinke C., Gaponik N., J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11790.
-
- Jiao M., Portniagin A. S., Luo X., Jing L., Han B., Rogach A. L., Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2200226.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
