Integration of Longitudinal Clinical, Immunologic, and Environmental Data for Enhanced Disease Monitoring and Management in Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Case Study
- PMID: 40212727
- PMCID: PMC11985163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2025.100358
Integration of Longitudinal Clinical, Immunologic, and Environmental Data for Enhanced Disease Monitoring and Management in Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Case Study
Abstract
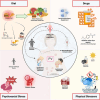
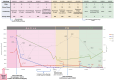
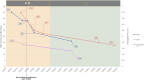
We present a case study of a patient with pemphigus vulgaris using an integrative, longitudinal approach to resolve the identities and potential contributions of a network of environmental exposures of possible clinical relevance in a genetically predisposed individual. Our comprehensive methodology tracked exposomal factors, disease evolution, and biological variables across the patient's lifespan. Our patient reported multiple predisease onset exposures historically associated with pemphigus vulgaris, including multiple psychosocial and physical/chemical stressors. After disease onset, despite standard pharmacologic treatment, disease activity fluctuated widely. Notably, within 14 months after substantial dietary changes and body mass index reduction, the patient achieved long-lasting complete clinical remission off therapy. Our results reinforce the significance of the gene-environment interplay in pemphigus vulgaris, emphasizing the role of diet in autoimmune regulation. This study serves as proof of concept regarding the power of detailed longitudinal mapping of disease expression and contemporaneous monitoring of the "exposome" and "behaviorome" to reveal previously unrecognized disease-modifying elements and suggest targeted and personalized lifestyle modifications to augment established treatments. Our study design and strategy offer a template for a hyperpersonalized approach to medicine through comprehensive lifespan data collection and integrative analyses to yield enhanced insights into disease development, with the goal of uncovering actionable interventions in future clinical care settings in the management of autoimmune disorders.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Exposome; Patient empowerment; Pemphigus; Personalized medicine.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The multifactorial complexities of autoimmune development in Pemphigus vulgaris: Critical evaluation of the role of environmental and lifestyle "exposome" factors.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1058759. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1058759. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36703956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oropharyngeal pemphigus vulgaris and clinical remission: a long-term, longitudinal study.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11(2):137-45. doi: 10.2165/11530050-000000000-00000. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20141235 Clinical Trial.
-
Temporal Outcomes after Rituximab Therapy for Pemphigus Vulgaris.J Invest Dermatol. 2022 Apr;142(4):1058-1064.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.09.013. Epub 2021 Oct 26. J Invest Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34710389 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of clinical and immunological factors associated with clinical relapse of pemphigus vulgaris in remission.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020 May-Jun;86(3):233-239. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_89_19. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020. PMID: 31898637
-
Role of Rituximab in the Treatment of Pemphigus Vulgaris: Patient Selection and Acceptability.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022 Nov 7;16:3035-3043. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S350756. eCollection 2022. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022. PMID: 36387051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ader R., Cohen N., Felten D. Psychoneuroimmunology: interactions between the nervous system and the immune system. Lancet. 1995;345:99–103. - PubMed
-
- Aghassi D., Dover J.S. Pemphigus foliaceus induced by psoralen-UV-A. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1300–1301. - PubMed
-
- Alpsoy E., Akman-Karakas A., Uzun S. Geographic variations in epidemiology of two autoimmune bullous diseases: pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol Res. 2015;307:291–298. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

