Comparative analysis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in China and worldwide based on the Global Burden of Disease study
- PMID: 40212838
- PMCID: PMC11983595
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1551672
Comparative analysis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in China and worldwide based on the Global Burden of Disease study
Abstract
Background: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in maintaining attention, excessive activity, impulsive behavior, and challenges in organizing and executing tasks. These symptoms can pose challenges in various settings, including home, school, and work, imposing a significant burden not only on affected individuals and their families but also on the global healthcare system.
Method: This study utilized open data from the Global Burden of Disease database covering the years 1990-2021 to analyze the characteristics of the burden of ADHD in China and worldwide, including incidence, prevalence, and adjusted lifespan for disability (DALYs). The Average Annual Percent Change (AAPC) and the corresponding 95% Confidence Interval (95% CI) were calculated using Joinpoint to reflect the trends in ADHD burden. A comprehensive comparative analysis of the differences in the burden of ADHD between China and the world was conducted in multiple dimensions, such as age and gender, using the R software. Statistical significance was indicated by a two-sided P-value of less than 0.05.
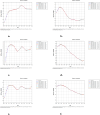
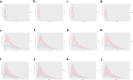
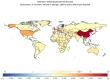
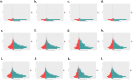
Result: From 1990 to 2021, the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of ADHD in China increased from 103.58 per 100,000 to 126.23 per 100,000, while globally, the ASIR decreased from 61.67 per 100,000 to 58.67 per 100,000. The age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR) in China increased from 1987.98 per 100,000 to 2183.99 per 100,000, contrasting with the global decline from 1228.35 per 100,000 to 1108.89 per 100,000. The age-standardized DALY rate (ASDR) in China also increased from 24.27 per 100,000 to 26.73 per 100,000, however, it decreased from 14.94 per 100,000 to 13.49 per 100,000 globally. The Average Annual Percent Change (AAPC) for ASIR, ASPR, and ASDR in China were 0.64%, 0.28%, and 0.29%, respectively, indicating an upward trend. In contrast, the global AAPC for the burden of ADHD showed a negative trend, with values of -0.16%, -0.34%, and -0.34% for ASIR, ASPR, and ASDR, respectively. The influence of age and gender on the burden of ADHD is distinct, with the highest incidence, prevalence, and DALYs typically observed during childhood. Furthermore, males consistently demonstrate higher rates across these metrics when compared to females.
Conclusion: While there has been a positive development in reducing the burden of ADHD globally, China faces a significant challenge with increasing rates. The focus on childhood and gender differences is crucial for tailored interventions and policies to address ADHD effectively.
Keywords: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder; China; Global Burden of Disease; disability-adjusted life years; incidence; prevalence.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Yang, Hu, Zhang, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of trend analysis of varicella zoster disease burden between China and the world 1990-2021 and disease burden forecast 2030.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 10;13:1535977. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1535977. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40129585 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal trends of thyroid cancer in China and globally from 1990 to 2021: an analysis of the global burden of Disease Study 2021.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 26;14(1):25538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77663-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39462100 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of trends in the burden of motor neuron disease in China, the United States, and globally from 1990 to 2021: projections for 2022-2041.Front Neurol. 2025 May 16;16:1539889. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1539889. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40452765 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and comparison of the trends in burden of rheumatic heart disease in China and worldwide from 1990 to 2019.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Oct 24;23(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03552-w. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37875798 Free PMC article.
-
Global and China trends and forecasts of disease burden for female lung Cancer from 1990 to 2021: a study based on the global burden of disease 2021 database.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb 8;151(2):68. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06084-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39921760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nourredine M, Gering A, Fourneret P, Rolland B, Falissard B, Cucherat M, et al. . Association of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in childhood and adolescence with the risk of subsequent psychotic disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. (2021) 78:519–29. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4799 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

