Microneedle-Integrated Device for Transdermal Sampling and Analyses of Targeted Biomarkers
- PMID: 40212914
- PMCID: PMC11936029
- DOI: 10.1002/smsc.202200087
Microneedle-Integrated Device for Transdermal Sampling and Analyses of Targeted Biomarkers
Abstract
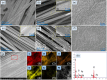
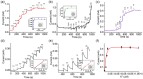
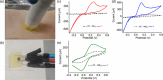
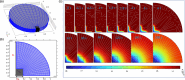
Currently available point-of-care systems for body fluid collection exhibit poor integration with sensors. Herein, the design of a disposable device for interstitial fluid (ISF) extraction as well as glucose, lactate, and potassium ion (K+) monitoring is reported on. It is minimally invasive and appropriate for single use, minimizing the risk of infection to the user. This microscale device contains a 3D-printed cap-like structure with a four-by-four microneedle (MN) array, bioreceptor-modified carbon fiber (CF)-sensing surface, and negative pressure convection technology. These features are incorporated within a compact, self-contained, and manually operated microscale device, which is capable of withdrawing ≈3.0 μL of ISF from the skin. MN arrays applied with an upward driving force may increase the ISF flow rate. Moreover, functionalized CF working electrodes (WE1, WE2, WE3) are shown to selectively detect lactate, glucose, and K+ with high sensitivities of 0.258, 0.549, and 0.657 μA μm -1 cm-2 and low detection limits of 0.01, 0.080, 0.05 μm, respectively. Ex vivo testing on porcine skin is used to detect the ISF levels of the biomarkers. The microscale device can be a replacement for current point-of-care diagnostic approaches.
Keywords: 3D printing; diffusion; glucose monitoring; interstitial fluids; microneedle arrays; transdermal.
© 2023 The Authors. Small Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Wearable microneedle array-based sensor for transdermal monitoring of pH levels in interstitial fluid.Biosens Bioelectron. 2023 Feb 15;222:114955. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114955. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023. PMID: 36462430
-
Enhanced Interstitial Fluid Extraction and Rapid Analysis via Vacuum Tube-Integrated Microneedle Array Device.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(21):e2308716. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308716. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38502884 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced extraction of skin interstitial fluid using a 3D printed device enabling tilted microneedle penetration.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 7;11(1):14018. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93235-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34234204 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle-Integrated Sensors for Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid and Metabolic Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 8;24(12):9882. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129882. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle-based devices for point-of-care infectious disease diagnostics.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Aug;11(8):2344-2361. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.010. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34150486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can we still use the Michaelis-Menten model for enzymatic microneedle sensors?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 29;122(30):e2418168122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2418168122. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40699925
-
Microneedle-aided nanotherapeutics delivery and nanosensor intervention in advanced tissue regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 3;23(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03383-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40319333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implantable bioelectronics and wearable sensors for kidney health and disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Jul;21(7):443-463. doi: 10.1038/s41581-025-00961-2. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40301646 Review.
-
Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Sensors for Fluid Monitoring: Advances and Challenges in Non-Invasive and Minimally Invasive Technologies.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 May 12;15(5):309. doi: 10.3390/bios15050309. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dervisevic M., Alba M., Yan L., Senel M., Gengenbach T. R., Prieto-Simon B., Voelcker N. H., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2009850.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
