Frequency of tremor in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40213512
- PMCID: PMC11982949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2025.100315
Frequency of tremor in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder causing various symptoms, including tremors, which significantly affect the quality of life and disability in people with MS (PwMS). Previous studies report a wide range of tremor frequency in PwMS, necessitating a comprehensive review for reliable estimates.
Objectives: This review aimed to elucidate the frequency rate of tremor among PwMS.
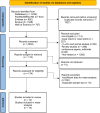
Method: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science up to April 27, 2024, to identify studies evaluating various types of tremors in PwMS. The Meta-proportion method implemented in R software version 4.0.0, utilizing a random-effects model, was employed to estimate the pooled frequency rates of tremor, with its 95% confidence interval (CI), among PwMS.
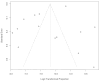
Results: From 3780 studies, 14 studies encompassing 17,458 PwMS (71.5 % female) were included. The mean age was 46.4 years, with a disease duration of 9.3 years and an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of 3.4. The pooled frequency of tremor was 33.32 % (95 % CI: 23.47 % to 44.88 %; I2 = 98 %; p-heterogeneity < 0.01). Subgroup analysis by sample size revealed that the pooled frequency of tremor in PwMS was significantly lower (p-value < 0.01) in studies with over 200 participants (22.46, 95 % CI: 15.69 % to 31.08 %, I2 = 99 %; p-heterogeneity < 0.01) compared to those with fewer than 200 participants (47.65, 95 % CI: 31.97 % to 63.81 %, I2 = 91 %; p-heterogeneity < 0.01).
Conclusion: Tremor is a prevalent complaint in PwMS. These findings highlight the necessity for targeted supportive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions to effectively address this prevalent issue in PwMS.
Keywords: Frequency; Multiple sclerosis; Tremor.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Fymat A.L. Multiple sclerosis: II. Diagnosis and symptoms management. J. Neurol. Psychol. Res. 2023;4:1–21.
-
- Simkins T.J., Duncan G.J., Bourdette D. Chronic demyelination and axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021;21:1–11. - PubMed
-
- McGinley M.P., Goldschmidt C.H., Rae-Grant A.D. Diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis: a review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021;325(8):765–779. - PubMed
-
- Elble R.J. Springer; 2017. Tremor.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous