Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) upregulation in the prediction of the malignant transformation risk in oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40213513
- PMCID: PMC11983453
- DOI: 10.3389/froh.2025.1578561
Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) upregulation in the prediction of the malignant transformation risk in oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to appraise, both quantitatively and qualitatively, the extant evidence regarding the role of EGFR upregulation in predicting malignant transformation risk associated with oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMD).
Methods: A comprehensive search was undertaken in the Web of Science, Embase, MEDLINE (via PubMed), and Scopus databases for longitudinal primary-level articles, whether prospective or retrospective in design, without restrictions on language or publication date. The QUIPS tool was employed for the purpose of assessing the potential for bias. A meta-analysis was conducted in addition to sensitivity analyses and analyses of the potential influence of small-study effects.
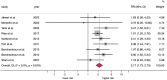
Results: In total, eight studies, which were treated as nine distinct units for analytical purposes, were included in the final sample, which encompassed 653 patients with OPMD with follow-up data. EGFR upregulation was found to be significantly associated with an elevated malignant transformation risk of OPMD (RR = 2.17, 95%CI = 1.73-2.73, p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses demonstrated that both EGFR protein overexpression (RR = 2.02, 95%CI = 1.55-2.63, p < 0.001) and EGFR gene amplification (RR = 2.70, 95%CI = 1.72-4.25, p < 0.001), nuclear staining (RR = 3.47, 95%CI = 1.50-8.01, p = 0.004) and the >10% cutoff point were significantly associated with transformation risk (RR = 2.27, 95%CI = 1.33-3.87, p = 0.003).
Conclusion: The present systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrates that EGFR overexpression, assessed through immunohistochemical technique, functions as a risk marker of OPMD malignant transformation risk.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024626482, identifier: CRD42024626482).
Keywords: EGFR; epidermal growth factor receptor; malignant transformation; meta-analysis; oral cancer; oral leukoplakia; oral potentially malignant disorders; systematic review.
© 2025 Cívico-Ortega, Ramos-García and González-Moles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Predictive Value of the Loss of pRb Expression in the Malignant Transformation Risk of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;17(2):329. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020329. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malignant transformation risk of oral lichen planus: A systematic review and comprehensive meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2019 Sep;96:121-130. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Oral Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31422203
-
Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 25;24(15):11888. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511888. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569265 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Role of EGFR/p-EGFR in Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 19;11:697369. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.697369. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34490092 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the predictive value of DNA aneuploidy in malignant transformation of oral potentially malignant disorders.J Oral Pathol Med. 2018 Feb;47(2):97-103. doi: 10.1111/jop.12603. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018. PMID: 28612463 Review.
Cited by
-
Hallmarks of Cancer Expression in Oral Leukoplakia: A Scoping Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 22;17(15):2427. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152427. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Warnakulasuriya S, Kujan O, Aguirre-Urizar JM, Bagan J V, González-Moles MÁ, Kerr AR, et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: a consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO collaborating centre for oral cancer. Oral Dis. (2021) 27(8):1862–80. 10.1111/odi.13704 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

