Evaluation of Nasal Reconstruction With Local Flaps Using the Translated Version of the FACE-Q Scale in a Local Language
- PMID: 40213748
- PMCID: PMC11984594
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80409
Evaluation of Nasal Reconstruction With Local Flaps Using the Translated Version of the FACE-Q Scale in a Local Language
Abstract
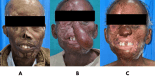
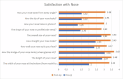
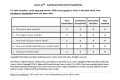
Introduction Attaining a nasal reconstruction that is functionally and aesthetically pleasing is a challenge to many reconstructive surgeons worldwide. Since the concept of the 'subunit principle' was laid down, many advancements have been devised in nasal reconstruction, but no proper evidence-based data is yet present in the literature regarding the satisfaction amongst patients after nasal reconstruction. In this study, we have evaluated the outcome after nasal reconstruction using a local language translation of FACE-Q scales. Materials and methods A total of 23 patients were operated on for nasal reconstruction in one or two stages during the period from September 2021 to December 2022, after assessing the cause, the subunit involved, and the type of nasal defect. The FACE-Q questionnaire was administered preoperatively and six months postoperatively to assess the satisfaction with outcomes among patients. Results Fifty-one nasal defects were reconstructed in 23 patients, out of which the nasal tip was the most commonly involved subunit. The defects were resurfaced with full-thickness skin grafts, V-Y advancements, deltopectoral flaps, nasolabial flaps, axial frontonasal flaps, and paramedian forehead flaps. Almost all the patients showed a significant improvement in their FACE-Q postoperative scales after the surgeries. Conclusion Nasal reconstruction, owing to its complex anatomy, has always been a subject of discussion. Comprehensive information about the outcome of nasal reconstruction can be measured using the FACE-Q scale, which is a patient-reported outcome assessment. The evaluation will always help the surgeon in regularly assessing and improving the outcome of surgery.
Keywords: face-q scale; nasal reconstruction; nasolabial flap; paramedian forehead flap; rhinoplasty.
Copyright © 2025, Sarkar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. ECR/BHU/Inst/UP/2014/RE-registration-2017dt 31.01.2017, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, UP, India issued approval 2020/EC/1905. Date of approval: 21.01.2020 The ethical committee meeting was held on 21.01.2020 at 3 pm in the chamber of the Dean, Faculty of Medicine, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi (India) for ethical clearance of the MD/MS/DM/M.Ch/Ph.D/synopsis/Projects submitted by the following: Dr. Arnab Sarkar Synopsis Title Evaluation of nasal reconstruction with local flaps using translated version of Face-Q scale in local language remarks: The Synopsis is approved by the Institute Ethics Committee . Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
[Cosmetic outcome of nasal tip reconstruction with the frontonasal flap and other locoregional flaps - Cosmetic Outcome of Nasal Tip Reconstruction].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2023 Aug;55(4):278-286. doi: 10.1055/a-2069-2246. Epub 2023 May 24. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2023. PMID: 37224879 Free PMC article. German.
-
Broadening applications and insights into the cross-paramedian forehead flap over a 19-year period.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019 May;72(5):763-770. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 25. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019. PMID: 30737127
-
A 10-year experience in nasal reconstruction with the three-stage forehead flap.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002 May;109(6):1839-55; discussion 1856-61. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200205000-00010. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002. PMID: 11994582
-
A Systematic Review and Overview of Flap Reconstructive Techniques for Nasal Skin Defects.Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 2021 Dec;23(6):476-481. doi: 10.1089/fpsam.2020.0533. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 2021. PMID: 33650884 Free PMC article.
-
Paramedian forehead flap reconstruction for nasal defects.Dermatol Surg. 2005 Aug;31(8 Pt 2):1046-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31829. Dermatol Surg. 2005. PMID: 16042928 Review.
References
-
- Nasal reconstruction after malignant tumor resection: an algorithm for treatment. Moolenburgh SE, McLennan L, Levendag PC, Munte K, Scholtemeijer M, Hofer SO, Mureau MA. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126:97–105. - PubMed
-
- The subunit principle in nasal reconstruction. Burget GC, Menick FJ. https://journals.lww.com/plasreconsurg/citation/1985/08000/The_Subunit_P.... Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;76:239–247. - PubMed
-
- Measuring patient-reported outcomes in facial aesthetic patients: development of the FACE-Q. Klassen AF, Cano SJ, Scott A, Snell L, Pusic AL. Facial Plast Surg. 2010;26:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Nasal reconstruction. Current overview. Fernandes JR, Pribaz JJ, Lim AA, Guo L. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;81:0–4. - PubMed
-
- Post-rhinoplasty outcomes in an Indian population assessed using the FACE-Q appraisal scales: a prospective observational study. Soni K, Patro SK, Aneja J, Kaushal D, Goyal A, Shakrawal N. J Laryngol Otol. 2020;134:247–251. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
