Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games
- PMID: 40214427
- PMCID: PMC11987935
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14070473
Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games
Abstract
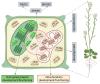
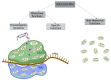
Ribosomal proteins (RPs) were traditionally considered as ribosome building blocks, serving exclusively in ribosome assembly. However, contemporary research highlights their involvement in additional translational roles, as well as diverse non-ribosomal activities. The functional diversity of RPs is further enriched by the presence of 2-7 paralogs per RP family in plants, suggesting that these proteins may perform distinct, specialized functions. The spatiotemporal expression of RP paralogs allows for the assembly of unique ribosomes (ribosome heterogeneity), enabling the selective translation of specific mRNAs, and producing specialized proteins essential for plant functioning. Additionally, RPs that operate independently of ribosomes as free molecules may regulate a wide range of physiological processes. RPs involved in protein biosynthesis within the cytosol, mitochondria, or plastids are encoded by distinct genes, which account for their functional specialization. Notably, RPs associated with plastid or mitochondrial ribosomes, beyond their canonical roles in these organelles, also contribute to overall plant development and functionality, akin to their cytosolic counterparts. This review explores the roles of RPs in different cellular compartments, the presumed molecular mechanisms underlying their functions, and the involvement of other molecular factors that cooperate with RPs in these processes. In addition to the new RP nomenclature introduced in 2022/2023, the old names are also applied.
Keywords: plant cellular ribosomal proteins; plant development; ribosomal protein paralogs; ribosome heterogeneity; stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential Participation of Plant Ribosomal Proteins from the Small Ribosomal Subunit in Protein Translation under Stress.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 21;13(7):1160. doi: 10.3390/biom13071160. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509195 Free PMC article.
-
Expression changes of ribosomal proteins in phosphate- and iron-deficient Arabidopsis roots predict stress-specific alterations in ribosome composition.BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 13;14:783. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-783. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24225185 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of ribosomal proteins reshapes the transcriptional and translational landscape in human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jul 8;50(12):6601-6617. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac053. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35137207 Free PMC article.
-
Translational control through ribosome heterogeneity and functional specialization.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Jan;47(1):66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34312084 Review.
-
Does functional specialization of ribosomes really exist?RNA. 2019 May;25(5):521-538. doi: 10.1261/rna.069823.118. Epub 2019 Feb 7. RNA. 2019. PMID: 30733326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

