Huntingtin-Interacting Protein 1-Related (HIP1R) Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblast Invasiveness
- PMID: 40214437
- PMCID: PMC11987873
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14070483
Huntingtin-Interacting Protein 1-Related (HIP1R) Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblast Invasiveness
Abstract
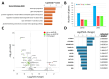
Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related (HIP1R) shares some function similarities with HIP1, and HIP1 regulates arthritis and RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) invasiveness. Therefore, we hypothesized that HIP1R might be involved in the regulation of FLS phenotypes and molecular processes relevant to RA. siRNA was used to knockdown HIP1R, HIP1 or control in RA FLS, followed by cell studies for invasion in Matrigel, migration, proliferation, and adhesion. RNA was sequenced and analyzed. HIP1R knockdown significantly reduced RA FLS invasiveness and migration (p < 0.05). The DEGs in siRNA HIP1R had an enrichment for GO processes "astrocyte and glial cell projection", "small GTPase signaling", and "PDGFR signaling". The most significantly DEGs had decreased expression in siRNA HIP1R and included AKT1S1, GABBR2, GPR56, and TXNDC12. siRNA HIP1 RA FLS had an enrichment for the "Rap1 signaling pathway" and "Growth factor receptor binding". The most significantly DEGs in HIP1 siRNA included FGF2, PGF, and SLC39A8. HIP1R and HIP1 DEG lists had a greater than expected number of similar genes (p = 0.0015), suggesting that, despite the major differences detected, both have partially overlapping functions in RA FLS. The most significantly DEGs in both HIP1R and HIP1 analyses are involved in cancer cell behaviors and outcomes. HIP1R is a new gene implicated in RA FLS invasiveness and migration, and regulates unique pathways and cell processes relevant to both RA as well as cancer biology. Our study provides new insight into processes implicated in FLS invasiveness, which is relevant for joint damage in RA, and identify new potential gene targets for FLS-specific treatments.
Keywords: HIP1; HIP1R; fibroblast; rheumatoid; signaling; synovial; synovitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KIF1C and new Huntingtin-interacting protein 1 binding proteins regulate rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes' phenotypes.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 25;15:1323410. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1323410. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38726004 Free PMC article.
-
Huntingtin-interacting protein 1 (HIP1) regulates arthritis severity and synovial fibroblast invasiveness by altering PDGFR and Rac1 signalling.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Nov;77(11):1627-1635. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213498. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 30049830
-
DLX4 regulates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes invasiveness and a cancer transcriptomic signature.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 11;15(1):25164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08960-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40645995 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase gene BIRC3 modulates TNF-induced cell death pathways and promotes aberrant proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1433898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433898. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Huntingtin-interacting protein 1 in cancer progression: a path less explored.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 15;42(5):164. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02698-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40232352 Review.
References
-
- van Zeben D., Breedveld F.C. Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1996;44:31–33. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F., Mitchell D.M., Sibley J.T., Fries J.F., Bloch D.A., Williams C.A., Spitz P.W., Haga M., Kleinheksel S.M., Cathey M.A. The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:481–494. - PubMed
-
- Nishimoto N., Hashimoto J., Miyasaka N., Yamamoto K., Kawai S., Takeuchi T., Murata N., van der Heijde D., Kishimoto T. Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): Evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an X ray reader-blinded randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007;66:1162–1167. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

