Oxidative Stress and Redox Imbalance: Common Mechanisms in Cancer Stem Cells and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 40214466
- PMCID: PMC11988017
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14070511
Oxidative Stress and Redox Imbalance: Common Mechanisms in Cancer Stem Cells and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
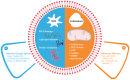
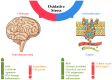
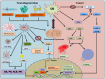
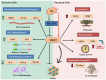
Oxidative stress (OS) is an established hallmark of cancer and neurodegenerative disorders (NDDs), which contributes to genomic instability and neuronal loss. This review explores the contrasting role of OS in cancer stem cells (CSCs) and NDDs. Elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) contribute to genomic instability and promote tumor initiation and progression in CSCs, while in NDDs such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, OS accelerates neuronal death and impairs cellular repair mechanisms. Both scenarios involve disruption of the delicate balance between pro-oxidant and antioxidant systems, which leads to chronic oxidative stress. Notably, CSCs and neurons display alterations in redox-sensitive signaling pathways, including Nrf2 and NF-κB, which influence cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Mitochondrial dynamics further illustrate these differences: enhanced function in CSCs supports adaptability and survival, whereas impairments in neurons heighten vulnerability. Understanding these common mechanisms of OS-induced redox imbalance may provide insights for developing interventions, addressing aging hallmarks, and potentially mitigating or preventing both cancer and NDDs.
Keywords: antioxidant; autophagy; cancer stem cells; ferroptosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; neurodegenerative diseases; oxidative phosphorylation; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; redox imbalance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vera-Ramirez L., Sanchez-Rovira P., Ramirez-Tortosa M.C., Ramirez-Tortosa C.L., Granados-Principal S., Lorente J.A., Quiles J.L. Free radicals in breast carcinogenesis, breast cancer progression and cancer stem cells. Biological bases to develop oxidative-based therapies. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2011;80:347–368. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2011.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zabel M., Nackenoff A., Kirsch W.M., Harrison F.E., Perry G., Schrag M. Markers of oxidative damage to lipids, nucleic acids and proteins and antioxidant enzymes activities in Alzheimer’s disease brain: A meta-analysis in human pathological specimens. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018;115:351–360. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.12.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

