B7H3 in Gastrointestinal Tumors: Role in Immune Modulation and Cancer Progression: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 40214484
- PMCID: PMC11988818
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14070530
B7H3 in Gastrointestinal Tumors: Role in Immune Modulation and Cancer Progression: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
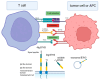
B7-H3 (CD276), a member of the B7 immune checkpoint family, plays a critical role in modulating immune responses and has emerged as a promising target in cancer therapy. It is highly expressed in various malignancies, where it promotes tumor evasion from T cell surveillance and contributes to cancer progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance, showing a correlation with the poor prognosis of patients. Although its receptors were not fully identified, B7-H3 signaling involves key intracellular pathways, including JAK/STAT, NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, and MAPK, driving processes crucial for supporting tumor growth such as cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis inhibition. Beyond immune modulation, B7-H3 influences cancer cell metabolism, angiogenesis, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, further exacerbating tumor aggressiveness. The development of B7-H3-targeting therapies, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, and CAR-T cells, offers promising avenues for treatment. This review provides an up-to-date summary of the B7H3 mechanisms of action, putative receptors, and ongoing clinical trials evaluating therapies targeting B7H3, focusing on the molecule's role in gastrointestinal tumors.
Keywords: B7H3 (CD276); gastrointestinal cancers; immune checkpoint; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bolandi N., Derakhshani A., Hemmat N., Baghbanzadeh A., Asadzadeh Z., Afrashteh Nour M., Brunetti O., Bernardini R., Silvestris N., Baradaran B. The Positive and Negative Immunoregulatory Role of B7 Family: Promising Novel Targets in Gastric Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:10719. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910719. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials